If your property has a plot of land that is not used for its intended purpose or with prefabricated structures located on it, then such a prospect as the organization of a warehouse is the best option for the rational use of this property. Having made a decision, first of all, the question arises, where should one start?
It is enough to imagine only the scale of future activities for the near future. The reason for this approach is the versatility of the chosen direction. affect the entire spectrum of economic activities of modern business, which means that there is a constant modernization of equipment, expanding the list of services and improving approaches to management and organization of the process.
The scale of future activities refers to the volume of estimated turnover, and most importantly, the amount that will be invested in the project. When all the preparatory activities are completed, you should proceed with specific actions. It will be of great help to first obtain the support of competent persons who have experience in creating such objects.
Initial stages
In any case, the following steps must be completed:
- to carry out elaboration of project documentation in all areas of the planned work;
- to carry out all construction and repair work, to control the quality of the construction of new structures or the repair of an existing fund;
- procure the necessary equipment to complete the warehouse;
- get permits for putting warehouse into operation;
- hire and, if necessary, train personnel who will serve the warehouse.
To erect storage facilities, first you need to draw up a project of buildings and structures in accordance with the requirements of the architecture department, to provide the territory with all the necessary communications, such as water, gas, sewage, electricity, the Internet. Then, you need to find a construction and installation company that will carry out all the necessary construction and repair work on this project. This company must have appropriate permits, a license, positive reviews and skilled workers.
The next step will be the procurement of primary and secondary storage equipment. It includes: racks, pallets, boxes, freight carts, tables, chairs. If necessary, automation of the accounting process is acquired: barcode scanner, database terminals, computer equipment and other things necessary for the implementation of the procedure for temporary storage of goods in a cargo storage warehouse. To implement an extended list of warehouse services, you will need loading equipment (cranes, forklifts, mechanical trolleys). It is mandatory to purchase equipment for video surveillance, sanitary and fire protection.
The organization of a warehouse of seasonal things in the field of commissioning of warehouse premises ends with the receipt of permits from state oversight bodies. One of these documents is the Act of inspection of a temporary storage warehouse (TSW) for compliance with veterinary and sanitary requirements. These include the requirement to ensure safe and comfortable working conditions for personnel (microclimatic and sanitary conditions), compliance with fire and anti-epidemiological standards.
Organization of labor and workflow
So, storage facilities have been built, storage equipment has been purchased and installed, permits have been obtained. The organization of the workflow at the warehouse includes:
- Drafting job descriptions;
- Directly, the process of hiring and, if necessary, training workers;
- Choice of a warehouse management system (TSW) and basic approaches;
- Organization of the internal warehouse regime;
- Organization of workflow;
- Organization of a reporting and reward system.

The successful organization of a warehouse for storage of goods is feasible only with qualified personnel, which should become one of the most important assets of the enterprise. Without making a mistake in choosing this team link, you can quickly get the predicted result of the growth of the main quality indicators of work. A lot of attention needs to be paid to staffing and clearly differentiating their responsibilities with job descriptions. If necessary, they need to be trained, or advanced. This process requires additional material investments. Ultimately, these relatively small costs will pay off and will help to avoid various errors, to optimize the volume of the staff by automating some technological and business processes.
The number of employees hired should be optimal and balanced. With a shift in equilibrium, you can get a situation of total irresponsibility or a regime of constant emergency. And one and the second options adversely affect the quality of the work performed, provokes staff turnover. All this, ultimately, leads to additional material costs for training and adaptation of a beginner, compensation for losses. It is also not worth actively saving on staff salaries. This factor, again, provokes staff turnover, unhealthy psychological state of the team and lack of motivation.
Choosing a warehouse management technique

Nowadays, often the organization of the warehouse is based on the address method. Address storage in a warehouse is very important where there is a large assortment of goods, which means that we will focus on it. In address warehouses, goods are stored in cells that have their own unique number. At the same time, control over the movement of goods is greatly simplified, the route of its movement, and control over storage conditions are optimized. The use of automated warehouse complexes by default implies targeted storage, as the movement of goods is controlled by automatic manipulators without human intervention. A high level of automation can significantly increase work efficiency with a slight increase in the level of costs and expenses.
If the enterprise has several warehouse premises spaced geographically, then in-house movements between them are possible. This approach is often justified with complex forecasting of the dynamics of demand for the storage service. Due to unbalanced demand, there are likely cases of shortage or excess of free space, which is quickly corrected by internal storage.
Inventory in the area of \u200b\u200bstorage areas should be carried out without fail. The optimal frequency is considered - at least once a month. This event is aimed at identifying theft and flaws in the personnel management system (poor quality acceptance of goods, resorts, errors in the quantity of goods in the package, and other shortcomings).
The address warehouse is usually divided into three conditional zones. In the first zone, unloading is performed, initial sorting and determining which storage zone the goods will be sent to in the future. The second zone is the place where goods stored in special storage bins are stored. In this zone, everything is clearly divided into rows and pallets. Racks and shelves are clearly numbered. Each shelf is divided into several cells, which also have their own serial numbers. In the third zone, goods intended for dispatch are completed and sorted.
The main advantage of the address method is that to carry out operations at any stage, personnel need a minimum of information, since all the address information of the goods is recorded in the documents. For example, at the time of acceptance of the goods, an address has already been put down in the receipt document where each type of goods should be specifically placed. And when completing the order, the employee is given an assembly sheet, where the addresses of the necessary goods are already clearly marked. In targeted warehouses, the influence of the human factor on the work process is minimized.
Organization and maintenance of accurate workflow
Nowadays, almost all documentation is maintained in programs such as 1C Warehouse Accounting, which have everything from a contract for storage of goods and receipts and consumables to price lists. Reliable accounting and process control is the key to future success.
As can be seen from the above, the organization of the warehouse is a complex and multifaceted process. Tackling it alone is beyond the power of anyone. Therefore, the best option would be to attract companies that provide warehouse outsourcing. Such a company will be able to organize work to create a specific business in a short time and on a turnkey basis. The work of specialists on this issue will help to provide for bypassing the "pitfalls" and to avoid additional costs.
The functioning of all components of the technological process in the warehouse should be interconnected. This approach promotes a clear coordination of the activities of all warehouse services, and also underlies the planning and control of the transportation of goods in the warehouse with minimal cost. Conventionally, the whole process can be divided into several components:
1) the organization of procurement and coordination of the relevant services;
2) cargo handling as such and processing of its documentation;
3) coordination of the sales service.
The coordination of the procurement service is carried out in the course of actions to provide products and as a result of supply chain management. The main point of supplying stocks is to provide the warehouse with products or raw materials in accordance with the potential possibilities of its processing at the current moment with full satisfaction of customer orders. In this connection, the establishment of the need for the acquisition of stocks must be fully agreed with the sales service and the actual capacity of the warehouse.
Stages of the technological process in the warehouse.The stage of registration of relations between the supplier and the client concerns all functions and operations, with the exception of the production process. This may include the receipt of the order and its execution, the delivery process, i.e., the actual execution of the order. Warehouse workers are required to own a large number of diverse operations because their responsibilities are determined by various areas, including financial and sales.
Accounting and control of incoming products, as well as dispatch of orders, helps to ensure uniformity of service for freight flows, maximize the use of available warehouse space and the necessary storage parameters, reduce the shelf life of stocks, as well as intensify warehouse turnover.
The list of services sold by different warehouses has significant differences; accordingly, the systems of warehouse operations will be different. Consider the list of warehouse services carried out in wholesale warehouses, which includes:
unloading vehicles;
product acceptance;
cargo movement inside the warehouse;
product placement;
selection of products from storage areas;
picking and preparing products for loading;
loading.
Loading and unloading operations the logistics process is more concerned. Unloading is an operation of a warehouse technological process, which consists in emptying a vehicle from cargo.
The technology for loading and unloading at the warehouse is determined by the nature of the cargo, the type of vehicle, and the means of mechanization used.
The next operation, which is important for the integrated logistics process, is the acceptance of the arrived goods in quantity and quality.
Decisions on the organization of material flow are made depending on the processing of the information flow, which often incorrectly displays the quantitative and qualitative composition of the material flow. In the process of various technological operations, unforeseen changes, excess losses, etc. may occur as part of the material flow. In addition, miscalculations of the supplier’s personnel when completing batches of shipped goods are possible, as a result of which shortages, surpluses, and mismatch of the assortment are not excluded.
During the acceptance, it is required to compare the actual figures of the arrived cargo with the data of the shipping documents. This allows you to adjust the information received. Maintaining the necessary information about the quantity and quality of cargo in the warehouse contributes to acceptance at all stages of the logistics process.
When unloading vehicles and accepting products, one should bear in mind the clauses of the agreement that are directly related to the delivery. In accordance with them, loading platforms for a specific vehicle and all the loading and unloading equipment that may be needed are prepared in advance. Today, unloading in warehouses is carried out on specially equipped unloading transport sites. The special equipment of the areas where vehicles are unloaded and the right choice of loading and unloading equipment facilitate unloading in the shortest possible time and with minimal cargo loss, which reduces transport downtime and, consequently, reduces handling costs. This allows you to achieve maximum process efficiency in the warehouse.
Labor operations in the warehouse.The operations carried out at this stage consist of the following components:
unloading vehicles (trucks, containers, wagons, etc.);
control of formal and actual compliance of delivery orders;
paperwork for the arrived products through the information system, which, by the way, allows for delivery in the shortest possible time and at the lowest cost;
creation of a warehouse freight unit. Its dimensions, as well as equipment for loading warehouse cargo units, transportation, unloading and storage, must be consistent with each other. This contributes to the efficient use of the material and technical base of the members of the logistics process at all stages of the movement of material resources, semi-finished products and finished products.
Standard pallets of 1200-800 and 1200-1000 mm in size are used as a base for the formation of a cargo unit. Any cargo in standard shipping packaging is not difficult to place on these pallets. A similar effect is achieved by the uniformity of the dimensions of the transport packaging.
In the warehouse, the goods accepted in quantity and quality are moved to the storage area.
Moving cargo inside the warehouse involves the transportation of material stocks between different areas of the warehouse: from the unloading ramp to the acceptance zone, from there to the storage, packaging and loading structure. This operation is carried out using hoisting-and-transport machines and mechanisms. Transportation of products in the warehouse should take place in a minimum time and the shortest route. This should help to avoid returning to any of the storage areas and unproductive operations. It is necessary to strive to minimize the number of product overloads from one type of equipment to another.
During storage, the cargo is placed and stored. The fundamental principle of rational storage is the efficient use of storage facilities. This is achieved by the optimal choice of storage organization, warehouse technology and equipment. The equipment of the warehouse for storage should correspond to the characteristic features of the cargo and contribute to the maximum use of the height and area of \u200b\u200bthe warehouse. At the same time, the area under the working walkways should be minimal, but suitable for the normal operation of hoisting-and-transport machines and mechanisms. For example, packaged goods can be held on racks or in stacks.
In order to streamline the storage of inventories and place them in the most rational way, they use a system of targeted (fixed) storage or free (products are placed in any free place) choice of a storage zone.
The process of warehousing and storage includes:
bookmarking inventories for storage;
storage of inventories and maintenance of factors suitable for this;
inventory of stocks in the warehouse, performed through the information system.
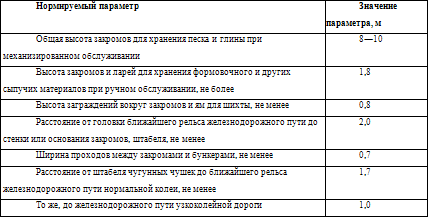
For example, consider the storage methods of molding and charge materials presented in table 1.
Table 1. Methods of storage of molding and charge materials
The main safety requirements for the storage of molding and charge materials are presented in table 2.
Table 2. Basic safety requirements for the storage of molding and charge materials
Usually the products sold are a small part of the assortment, therefore it is better to place them in convenient places, extremely close to the vacation areas, parallel to the areas where the traffic is most intense.
Acceptance and dispatch of products from the warehouse can be performed on one combined site, but can be spatially separated (Fig. 3).

Fig. 3. Separation of flows in stock
Products, the need for use of which does not occur often, are placed parallel to the zones where the traffic is least intense. Larger goods and products stored without packaging can also be located along such zones, since the movement of these inventories is usually associated with certain difficulties.
An interesting example is given by A. M. Gadzhinsky. He considers a warehouse, the assortment of which includes 27 items (Table 3, items a, b, c, ..., i). The products in this example are located in the rack equipment on pallets in a packaged form, dispensed with whole cargo packages, and all operations with it are completely automated. In total, 945 freight packages were released in the previous period.
Table 3. Implementation for the previous period 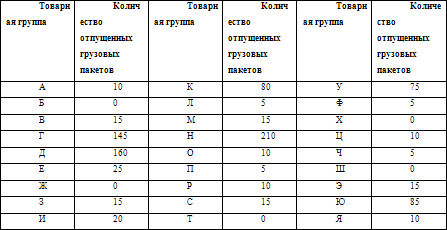
In this example, almost all ordered goods amounted to 6 assortment items (items n, d, d, q, y, y). A. M. Gadzhinsky emphasizes that “when placing stock in a warehouse without taking into account the speed of turnover of different items, the total mileage of equipment during storage and selection increases by 2–3 times.” There is no doubt that the products according to the most demanded items of the assortment should be placed in areas where freight traffic is most intense.
Another operation in the technological process at the warehouse is the selection of goods from the storage area. It can be realized in two key ways:
selection of a full cargo package;
selection of a share of a package without displacement of a pallet.
The execution of a consumer order begins with the selection of inventories in storage areas. The selection is carried out in accordance with the invoice or selection sheet.
Methods of product selection:
individual selection(for one customer) is a sequential acquisition of each order separately. In case of individual selection, the goods are immediately packaged; upon completion of the selection procedure, they are checked and sent to the recipient;
comprehensive selection(for several customers) is a selection of products for several consumers at the same time according to the general selection list; The picking is carried out from the mass of the most diverse storage units of a certain assortment, which is currently in stock, in accordance with the consumer order.
This operation can be fully mechanized or performed using small-scale mechanization.
As mentioned above, warehouses differ from each other in terms of mechanization and technical equipment. Mechanized selection is mainly used in large warehouses and terminals. Inventories packaged on a pallet are removed by means of a mechanism from the stacking area and are transferred to the picking area in the form of a full transport unit. Indoors, railless vehicles are usually used, and on open-air platforms, mechanisms running on gasoline, diesel fuel or gas. Forklifts, bridge and gantry cranes, etc. can be used.
At automated warehouses, selection is carried out using automated means - such as rack-mounted stacker cranes, robocars, etc. Manual selection is carried out when dispensing an insignificant volume of products, small-piece goods of a complex assortment stored on shelves.
In statistical warehouses, the selector moves parallel to the rack cells in a specialized rack lift, selecting the required products.
In high-altitude dynamic warehouses, a rack-mounted elevator without the participation of an employee is fed into the cells with the required load. By means of a telescopic forks, the package with the cargo is removed from the storage place and transported to the selector's workstation. The necessary part of the inventory is selected, the balance is returned to the place of storage.
Height statistical warehouses, as a rule, does not exceed 12 m. The length of the shelves is not mandatory, but the ratio 1/5 is considered to be the most suitable.
Dynamic warehousesusually larger than statistical. The height of the racks can vary from 25 to 40 m, and the length - up to 150 m.
The picking process is the preparatory work for the product according to consumer requests.
The assembly and shipment of ordered products includes the following steps:
receipt of a consumer order (selection list);
selection of goods of each item in accordance with the selection list;
individual packaging of selected products for a specific consumer in accordance with his order;
preparation of cargo for shipment (packaging, laying on a carrier);
paperwork for finished products and the implementation of control of preparation of the order;
combining consumer orders into a single transport batch and filling out invoices;
delivery and stacking of cargo in a vehicle.
Commissioning of consumer orders is carried out in the picking area. Paperwork is carried out through the information system. If the wound system is targeted, the place of the selected product is displayed in the selection sheet. This allows you to reduce the time of selection and helps to track the issuance of inventories from the warehouse.
The information system simplifies picking and contributes to the optimal use of the vehicle by combining cargo into an economical lot. At the same time, the best delivery route is selected. Shipment is carried out at a special loading and unloading site (the requirement for efficient shipment is almost the same as the requirements for unloading).
If the wholesale company itself delivers the products to the client from the warehouse, then on the site located separately from the main warehouse premises, a shipping expedition should be organized where the material stocks prepared for shipment will be concentrated and their delivery to customers will be ensured.
The technological process at the warehouse ends loading operation. The selected products are moved to the picking area of \u200b\u200bconsumer orders, where the correctness of the selection of warehouse units in accordance with customer orders is controlled. Then the cargo is packed in reusable packaging. A packing list is laid in each unit of inventory, the existence of which enhances the responsibility of warehouse employees for the accuracy of picking a batch and activates the process of product acceptance in stores. Inventory containers with cargo are sealed and sent on an expedition where picking consignments is carried out along a pre-planned route to the destination according to the location of specific customers.
When organizing such shipments, the carrying capacity of the vehicles used must be taken into account. Ready-made batches of products during the expedition are recorded in a special journal, in which the customer is recorded, number, date of issue and invoice amount, number of places to be sent, tare numbers. The head of the expedition confirms with signature the acceptance of products for dispatch. After the return of payment claims - orders with the receipt of the consignee of the goods, a corresponding entry is made in the journal. The expedition orders a vehicle and organizes the shipment of products to the customer.
Sample written application of the customer, attached to the contract of transport expedition
dated "___" _______ 2008 N___
Please consider shipping
Route
Departure city
Destination City
___________________________________________
Transport
___________________________________________
Planned Shipment Date
___________________________________________
Cargo Information
Nature of the cargo
___________________________________________
Total: cargo weight (kg) / cargo volume (m 3)
___________________________________________
Number of places / Maximum: dimensions of one place (cm) / weight of one place (kg)
___________________________________________
Nature of packaging
___________________________________________
Special Delivery Terms
___________________________________________
Enter into an insurance contract / declare insurance value (RUB)
___________________________________________
Call a courier with a car
___________________________________________
Shipping Address
(if calling a courier with a car)
___________________________________________
Detailed address
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
The contact person
___________________________________________
Sender
___________________________________________
Detailed address
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
The contact person
___________________________________________
Recipient
___________________________________________
Detailed address
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
The contact person
___________________________________________
additional information
Who pays for the shipment
___________________________________________
Form of payment
___________________________________________
Payer details (TIN, KPP)
___________________________________________
Please inform us about information on shipment (contact person, phone)
___________________________________________
Please send invoices and acts of completed work to the address (index required)
___________________________________________
I filled out an application
Full Name
___________________________________________
Contact phone
___________________________________________
Packing list sample
The packing list is in free form, but it must include strictly defined information.
1. Name of products.
2. Marking, part numbers, etc.
3. Net / gross weight.
4. Quantity.
5. Type of inventory.
6. The number and type of packages.
7. Signature of the person in charge, seal of the organization.
Products prepared for shipment are forwarded to the loading area. The cargo is placed in a vehicle, taking into account the efficiency of using its area, as well as taking into account the route.
With any existing process of production and distribution of material assets, a warehouse inevitably arises. This rule applies to any sector of the economy and business, and at present, the cost of "production" of a product sometimes amounts to only 30% of the final price, and the remaining 70% has a significant share of the warehouse and everything connected with it. That is why the warehouse in the structure of any company should be given significant attention.
From traditionally secondary, the warehouse has become a key link, capable of both increasing profits and nullifying all the achievements of a successful enterprise. The reason is the widespread competition and, as a result, the desire to reduce overhead as a whole, including due to the optimal organization of the warehouse. It is estimated by economists that with well-developed production, the same amount of investments in the company's core business and in the warehouse gives significantly higher returns when investing in warehousing, which, as a rule, has significant reserves for increasing efficiency.
Two identical warehouses do not exist, therefore, all recommendations that are true in the general case must be correctly adapted to each specific one.
The purpose of these materials is to give the right approach to the general organization of the warehouse and the selection of technological equipment for this.
The territory of the warehouse
The warehouse complex itself begins with the adjacent territory, which is no less important than the building itself. There should be enough space for maneuvering and setting up transport for loading / unloading, and if technology requires it, vehicle sediment.
The most modern, well-equipped warehouse will be ineffective if vehicles are stuck in traffic jams at the entrance to it or with difficulty maneuvering on its territory. It is advisable to organize the movement so that the incoming and outgoing traffic flows do not interfere with each other.
During the construction of a new warehouse, it is worth considering the possibility of its further expansion in the future, for which, accordingly, the loading and unloading front should be located. This will not affect the current operation of the already launched part of the warehouse, but will save significant funds with further expansion of the complex.
Loading and unloading front
There are two fundamental approaches to the equipment of the loading front - the floor of the warehouse is raised (ramp) and - the floor of the warehouse is at ground level (cargo rises to the side of the machine). The second option is undoubtedly cheaper and easier to build - this is its main advantage.
With this organization of work in the shipment area, classic loaders are usually used, less common Rich truck (stacker trucks with retractable carriage), and stackers with telescopic forks. This method of loading can be recommended for low cargo turnover or working with non-standard cargo packages in terms of size and weight.
In all other cases, it does not provide intensive work, since the loader needs to lift the load to a height of about 1 meter and turn it perpendicular to the side of the machine, which takes a certain amount of time.
In the case of unloading the wagon through the rear doors, you will have to “launch” movers with a hydraulic trolley into the car, which will pull the load to the edge of the machine - because only there you can take it with a loader or a stacker.
Therefore, warehouses with a floor at ground level can be recommended as an economically viable solution if the warehouse has a low cargo turnover and long parking of unloaded vehicles can be allowed.
Currently, despite the increase in the cost of capital structures, the vast majority of modern warehouses are being built with a loading ramp. In this case, the warehouse floor is elevated above ground level (usually 1200 mm), which allows the warehouse transport to drive directly into the car with cargo.
 Depending on the specifics of the work, there are three main types of setting transport for loading(see illustration).
Depending on the specifics of the work, there are three main types of setting transport for loading(see illustration).
When parking with the end face of the body, the maximum number of loading gates along the front of the ramp is achieved (the most common option). With lateral setting of the machine, access immediately to the entire body appears, which can be convenient when handling specific loads.
The presence of a ramp allows you to install additional equipment that significantly speeds up the process of loading and unloading. There are many ways to facilitate entry into the body - from the simplest drawbridges (often replaced by sheets of metal), swing-down balanced ramps, mounted on the edge of the flyover, to the most effective technical means that ensure that warehouse equipment can quickly travel inside the machine:
|
This is an electro-hydraulic equalizer (dock leveler), mounted directly in the gate range. Usually it is installed at a height of 1200 mm from the ground, while it is able to compensate for differences upward 400-600 mm and down 350-400 mm. Such a leveler in combination with maneuverable and efficient self-propelled pallet conveyors provides the most efficient loading and unloading front (see illustration). |
 |
|
|
For comparison, you can give an example. The daily turnover of the warehouse is 150 pallets. Three options are considered: from the ground level by a loader, from a ramp by a hydraulic trolley and from a ramp by a self-propelled pallet conveyor (see illustration). In the first case, the productivity is 23 pallets per hour, in the second - 17, in the third - 32 pallets per hour. Despite the largest initial investment, the third option is the most economically efficient and, with a high turnover, can save up to 20% in the warehouse shipment area. |
 |
In the general case, if the warehouse is equipped with a ramp and must provide a high cargo turnover, it is recommended to use self-propelled pallet transporters (see photo). |
|
|
And in the case of very high intensity - transporters with a platform for the operator, to speed up the process of unloading and moving the goods (see photo). |
A special case is represented by high production facilities, which are now often converted into warehouses. As a rule, the floor of such a “warehouse” is located at ground level, which is a big minus, but at the same time, high ceilings and large spans allow you to organize a good warehouse.
What can be done in this case to improve the situation in the shipment area? The solution is simple - raise the floor level in the doorway to the level of the car body. Sometimes hydraulic lifting tables are used for this purpose - but they do not provide high speed.
For really intensive work, it will be correct to build a ramp starting from the floor level of the warehouse and rising to the height of the car body to the gate alignment - this way the loader will be able to call directly into the car. However, the expensive area under the ramp inside the warehouse is lost.
 Therefore, another solution is used - in front of the loading ramp, a recess is made along the front of the warehouse, corresponding in depth to the floor height of the main shipping transport. This method has two limitations: the availability of sufficient space for transport maneuvers in front of the warehouse and the need for rain and melt water runoff (see figure).
Therefore, another solution is used - in front of the loading ramp, a recess is made along the front of the warehouse, corresponding in depth to the floor height of the main shipping transport. This method has two limitations: the availability of sufficient space for transport maneuvers in front of the warehouse and the need for rain and melt water runoff (see figure).
In both of the above methods of pseudo-ramp devices, it is possible to equip the loading and unloading gates with a standard set of equipment (gates, levelers, thermowells).
 Another bottom integral part of the loading front are the gates and the doorway seals in their range. The main types of sealants (or thermowells, dock shelters) are curtain, pillow and inflatable. Without dwelling on them in detail, we recommend for the temperate climate zone the curtain type of thermowells, as affordable and fully fulfilling its tasks.
Another bottom integral part of the loading front are the gates and the doorway seals in their range. The main types of sealants (or thermowells, dock shelters) are curtain, pillow and inflatable. Without dwelling on them in detail, we recommend for the temperate climate zone the curtain type of thermowells, as affordable and fully fulfilling its tasks.
For a climate zone with low winter temperatures, a curtain type is also quite suitable, but if funds permit, the most airtight inflatable type of sleeve hoses will be very effective, tightly compressing the body of a standing machine.
 Among the gates, the most convenient and versatile, and therefore sectional, are widespread, differing in the way of lifting (with and without electric drive) and the location of the folded part of the gate, which allows them to be installed in both high and low enough rooms.
Among the gates, the most convenient and versatile, and therefore sectional, are widespread, differing in the way of lifting (with and without electric drive) and the location of the folded part of the gate, which allows them to be installed in both high and low enough rooms.
 To separate the various temperature zones inside the warehouse in places of frequent passage of equipment, simple vertical curtains or recently acquired high-speed gates made of synthetic material, quickly folding into a roll above the doorway, are recommended.
To separate the various temperature zones inside the warehouse in places of frequent passage of equipment, simple vertical curtains or recently acquired high-speed gates made of synthetic material, quickly folding into a roll above the doorway, are recommended.
Floors in stock
A modern warehouse is a complex system consisting of many components and one of the fundamental ones is the floor. Unfortunately, this part of the warehouse is not always given sufficient importance and this error is expensive. Most often, modern floors use concrete floors with a top reinforcing layer of various types.
There are three basic requirements for floors:
evenness
no cracks
dust-free - similar to high-quality industrial floors.
Dust free - Abrasion resistance is important for several reasons. Firstly, a gradually accumulating layer of cement dust constantly settles on the stored cargo. Even special equipment at some point can’t cope with cleaning the premises, and cleaning the goods is extremely difficult. People working in the warehouse will constantly be in adverse conditions, which affects the health and productivity of labor - which means that the warehouse will not be able to work at full strength. In addition, the increased amount of dust adversely affects the state of warehouse equipment. In addition to purely mechanical wear (abrasive particles entering the bearings), machine control systems may fail, as an increased amount of dust falls into the electronic control units.
The situation is similar to the pollution of the central unit of a personal computer - those who ever opened the PC case had to remove plentiful dust accumulations, especially in the cooler area. Something similar happens in modern warehouse machines, also equipped with controllers and cooling fans, only the situation is much worse than that of a PC in the dirtiest place. Of course, this problem can be solved by daily cleaning with a vacuum cleaner, but not all parts of the machines are easily accessible and, in any case, additional time is spent on it.
No cracks is also an important requirement. It is mainly associated with increased wear on the wheels of equipment and, in the case of large cracks, with accelerated wear on the chassis. In addition, the speed of the equipment in such conditions is somewhat limited, which affects productivity. The absence of cracks is ensured by the correct selection of the concrete base (high-quality sub-base, proper reinforcement and sufficient thickness of the concrete slab itself).
In addition, when developing TK, the load experienced by them must be correctly indicated on the floors of a particular warehouse. Three-tier and six-tier racks are completely different loads, and the equipment serving them has different weights and its distribution.
 Evenness of the floors - Perhaps the most significant requirement, and most importantly, its failure to completely devalue quality non-dusting floors without cracks. The floor in the warehouse should not have a systematic bias (horizontal level), and also provide good "local evenness".
Evenness of the floors - Perhaps the most significant requirement, and most importantly, its failure to completely devalue quality non-dusting floors without cracks. The floor in the warehouse should not have a systematic bias (horizontal level), and also provide good "local evenness".
The first requirement is associated mainly with the stability of the racks, and with high lifting heights - and the stability of the equipment. The second condition, “local evenness,” is determined by the type of equipment operating in the warehouse. Floors of such quality were encountered when highly-lifting internal storage equipment with low clearance almost "sat down" on the base of the bulge of an uneven floor.
In general, for storage heights of up to 6 meters with classic wide (from 2.3 meters) aisles, floor flatness requirements are non-rigid (see photo).
Stackers with three-sided cargo handling, which work in narrow passages of 1600-1900 mm, are most critical to the floor. In this case, the following requirements must be observed:
The installation of good floors is a difficult task, so the main thing in this matter is not only strict observance of technology, but also the qualifications and experience of the personnel directly performing the work. The main criterion for choosing a contractor for this site should be successful experience in implementing projects with floor quality similar to the requirements of the planned warehouse. The best result is achieved when the contractor knows the load characteristics of equipment and racks, as well as their location on the site. In this case, it is possible to foresee the position of the shrink joints not in the middle of the driveway, as often happens, but under the racks; in addition, to exclude hit of supporting elements of power structures of racks on the technological joints of the floor (grips).
Finishing the topic of the device of the floor, I want to express a time-tested rule. When equipping a new warehouse, making a good quality floor during the construction phase will cost less (despite the significant initial cost) than subsequent repairs with a partial suspension of the existing warehouse. To this we can add the material losses listed above from working on low-quality floors.
Proper lighting is also an integral part of an efficient warehouse. It is advisable to place the luminaires above the inter-shelving aisles - so with the same number of lamps you achieve greater illumination. At the same time, lighting should not dazzle stacker operators (forklifts) looking up at the upper tiers of racks. To do this, some lamps can be sent to the roof - this will help to evenly illuminate the upper part of the shelves. The color scheme of the warehouse is also important. The standard solution is a light (almost white) roof, which improves overall lighting, slightly darkened walls and an even darker floor. And do not forget to monitor the serviceability and cleanliness of the fixtures.
Shelfless storage
This "system" is rightfully considered the most widespread and universal. It is simple and has a number of undeniable advantages. The main thing is to maximize the use of warehouse space in the complete absence of capital costs, which is very attractive. It is also important that practically any equipment can work in such a "system".
However, shelfless storage has significant drawbacks - difficult access to goods of various nomenclature and limited storage height (determined by the strength of the cargo packaging).
Classic front shelving
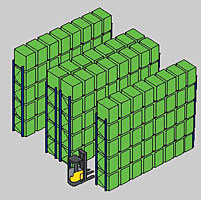 The most common system. It is a well-known shelving various heights on which pallets are loaded. The structures are carried out with different load capacities, depending on the planned loads, and the tier heights of modern bolt-free systems on hooks quickly change depending on the height of the pallet with the load.
The most common system. It is a well-known shelving various heights on which pallets are loaded. The structures are carried out with different load capacities, depending on the planned loads, and the tier heights of modern bolt-free systems on hooks quickly change depending on the height of the pallet with the load.
This is a truly universal and inexpensive solution that allows you to use almost any lifting equipment, and provides free access to any of the stored pallets with cargo.
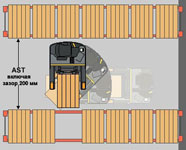
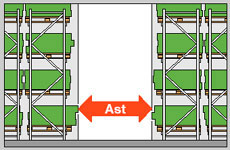
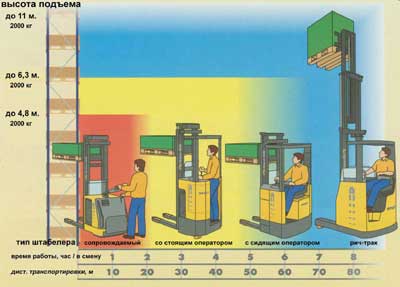
Depending on the type of equipment used, the width of the aisle between the racks (Ast) varies from 2.1 m (stacker) to 3.5 m (loader), and the height of the pallets of the upper tier of racks reaches 11 meters.
The equipment of the warehouse with front racks is practically devoid of flaws and is often optimal. The only serious drawback of the system is the insufficient use of the warehouse volume.
However, the relatively low capital and operating costs, combined with the provision of high cargo turnover, are often a decisive factor in favor of front shelving.
Equipment for front shelving
As already noted, serve front shelving possible with any lifting equipment with a pitchfork. The most universal and common tool is a forklift. Its main advantage - unpretentiousness to the floors and the ability to drive outside - is most often in demand in old buildings of small height.
The fact is that the loader has sufficiently large dimensions - the width of the inter-rack passage for setting pallets (Ast) for it is usually 3.1-3.5 m. This leads to the fact that most of the warehouse area is not used for storage of cargo, but for travel.
The use of stackers allows you to reduce the racks by about 1 meter and increase the storage height, which ultimately will significantly increase the storage capacity. But it is important to remember that good quality floors are required for the stacker to work.
The correct approach to the selection of lifting equipment is as follows:
Work with the floor plan and the development of various options for installing shelving.
Each option is developed based on the Ast indicator of the truck (loader) and the required lifting height.
Evaluation of options - the amount of capital costs (flooring, shelving, equipment) in relation to the result (warehouse capacity, possible cargo turnover ...).
On the stackers, as the main intra-warehouse lifting equipment, I want to dwell in more detail.
The simplest device for lifting pallets on racks is a manual hydraulic stacker with a lifting height of 1.5-2.5 m (usually they are serviced by two-tier racks). Stackers with manual movement and electro-hydraulic lifting have higher productivity. They are able to lift cargo to a height of 3.0-3.5 m and are usually used to service three-tier racks. Both types of stackers are good because they are relatively inexpensive, but they do not provide a high intensity of work - therefore, they are suitable only for warehouses with a small cargo turnover. If the warehouse should provide a significant amount of reception and shipment, self-propelled stackers are needed.
 The most common stackers in this class are stackers (they are also driven, with a rotary handle, "with a leash").
The most common stackers in this class are stackers (they are also driven, with a rotary handle, "with a leash").
They are made by almost all manufacturers of in-warehouse equipment, so choosing the right model according to technical parameters and price / quality ratio is quite simple. Two main types are distinguished - really accompanied stackers, behind which the operator goes and machines with a folding platform, standing on which the operator moves around the warehouse.
stacker trucks with a platform move faster around the warehouse (up to 8 km / h without load) and therefore are more productive - and this is their main advantage, but at the same time they have increased dimensions and in narrow inter-rack passages the operator sometimes has to fold the platform and control the machine from the floor. From the point of view of lifting height (up to 4.5-5.5 m) and carrying capacity, these machines differ slightly.
 A qualitative technological leap occurs during the transition to stackers with an operator standing or sitting in the cab.
A qualitative technological leap occurs during the transition to stackers with an operator standing or sitting in the cab.
The principle of operation is the same as that of the accompanied stackers - the support consoles are located directly under the forks. The main difference in the position of the operator, he is in the cabin protected from the sides and from above - thanks to this it is able to more effectively control the machine. If you add to this the increased speed of movement and lifting, the electric steering wheel and the ability to customize the workplace for a particular operator - it becomes clear why these machines have high performance.
Of course, equipment of this class is more expensive, but its purchase is justified by an increase in the amount of work carried out by one machine. It is also important that the lift height of these stackers reaches 6-6.5 meters with a residual load capacity of 1000-1500 kg and an inter-rack passage width of 2.3-2.5 meters. Accompanied stackers usually cannot provide this combination of performance.
 The most serious, “heavy” class of equipment for frontal racks is a stacker with a retractable carriage of a load-lifting mechanism or a Rich-truck.
The most serious, “heavy” class of equipment for frontal racks is a stacker with a retractable carriage of a load-lifting mechanism or a Rich-truck.
This machine is a kind of "hybrid": when the mast is retracted, it resembles a stacker, and when extended, it works like a classic loader, while simultaneously using the best qualities of both types of equipment.
The rich truck is one of the most sophisticated and high-performance internal storage machines. It provides high lifting and moving speeds (0.6 m / s and 12 km / h, respectively), it is able to lift pallets weighing 1.5-2.5 tons, while the residual capacity at an altitude of 11 meters can reach 1000 kg.
Of course, it is not economically feasible to use equipment with such capabilities at low altitudes, therefore reach trucks are usually used when working with racks above 7 meters. Sometimes there are applications for light models with a lift height of about 5 meters. This may be justified to provide special working conditions, the necessary carrying capacity or speed.
Rich tracks come in many modifications; in fact, the standard of the class is a double telescopic mast with a free lift and an integrated sideshift (lateral shift of the forks). By analogy with the loaders, the mast tilt is always present, but at elevations of more than 9 meters, the pitch tilt is used instead. In addition, each manufacturer has its own "highlight" in the design, so the choice of a machine is not easy and requires close communication with a competent specialist.
Double depth shelving
 By design, these are ordinary frontal racks with double rows. In cost, they are very close to the classic front ones, but to work with them requires equipment with telescopic forks. The main advantage of racks of this type is the better use of the warehouse area (under racks up to 50% of the total warehouse area), which is 25% more effective than when installing front racks. The speed of cargo turnover is somewhat reduced, but still remains quite high.
By design, these are ordinary frontal racks with double rows. In cost, they are very close to the classic front ones, but to work with them requires equipment with telescopic forks. The main advantage of racks of this type is the better use of the warehouse area (under racks up to 50% of the total warehouse area), which is 25% more effective than when installing front racks. The speed of cargo turnover is somewhat reduced, but still remains quite high.
The only serious limitation of the system is that only half of the pallets with cargo (external rack row) are directly accessible, and to remove the "inner" pallets, the outer one must first be removed (see figure).
If the majority of the product range is in stock in an amount of more than 2 pallets, then the system is quite applicable. Therefore, double-depth shelving is not suitable for companies with a very wide range of products and small quantities.
In all other cases, the system works very well and with the correct organization of the warehouse management system provides 80-90% occupancy of all available storage places (in classic front shelves - 95%).

 Most often, stackers with telescopic forks are used to work with double-depth shelving. Stackers with a standing or sitting operator in the cab can be used up to a lifting height of 6 meters, and reach trucks (up to 10 meters) (see the figure on the left).
Most often, stackers with telescopic forks are used to work with double-depth shelving. Stackers with a standing or sitting operator in the cab can be used up to a lifting height of 6 meters, and reach trucks (up to 10 meters) (see the figure on the left).
At the same time, for safe operation at elevations of more than 6 meters, a video camera (mounted on forks) and a TV monitor (in the operator's cab) are usually used - see the figure to the right.
In general, a double-depth shelving system will be justified if it is necessary to increase the capacity of a warehouse located on a limited area, while not spending a lot of money. And the advantage of the system, compared with front racks, is the same cost of the racks themselves and relatively inexpensive equipment (about 20% higher than conventional reach trucks). As a result, it is possible to achieve a 25% increase in warehouse capacity in the same area.
Narrow aisle shelving
 Warehouses organized using narrow aisle technology are some of the most complex and expensive. Despite the fact that the racks themselves are no different from the usual front racks, they can be slightly more expensive due to the requirements for dimensional accuracy of the rack structure itself, in addition, installation is much more expensive - very tight tolerances for the width of the aisle and the verticality of the rack, and the installation itself is technically more complicated due to the increased height of the structures.
Warehouses organized using narrow aisle technology are some of the most complex and expensive. Despite the fact that the racks themselves are no different from the usual front racks, they can be slightly more expensive due to the requirements for dimensional accuracy of the rack structure itself, in addition, installation is much more expensive - very tight tolerances for the width of the aisle and the verticality of the rack, and the installation itself is technically more complicated due to the increased height of the structures.
Another cargo storage system based on classic front shelves is shelves with narrow aisles (1.5-1.8 meters wide) designed for work special stackers.
The quality of the floor for a warehouse of this level was already mentioned in the previous article, in this case it is really a very important and expensive component. In addition, it is necessary to equip the side rail guides for the movement of the stackers along the inter-rack passage, which is also worth the additional cost.
Now about the special narrow aisle stackers. These are indeed some of the most modern and sophisticated warehouse machines. They are able to rotate the carriage with the forks 180 degrees and push the pallet into the depth of the rack by 1200 mm.
Two main types of equipment are used - with a stationary operator or with an operator lifting together with a load.
 In the first case, the control is carried out from a fixed cabin, the machine is equipped with a video camera and a TV monitor. And provides a rise to a height of 11 meters (see the figure on the left).
In the first case, the control is carried out from a fixed cabin, the machine is equipped with a video camera and a TV monitor. And provides a rise to a height of 11 meters (see the figure on the left).
 In the second case, the operator rises in the cab with the load and completely controls the process of lifting and moving. A high speed of operation is ensured due to the simultaneous lifting and movement along the aisle (diagonal movement), with a lifting height of up to 15 meters (see the figure on the right).
In the second case, the operator rises in the cab with the load and completely controls the process of lifting and moving. A high speed of operation is ensured due to the simultaneous lifting and movement along the aisle (diagonal movement), with a lifting height of up to 15 meters (see the figure on the right).
The main advantage of a narrow aisle storage system is the good use of the storage area (under racks up to 55% of the total area), while high-altitude storage is possible, which further increases the storage capacity. In addition, each cargo package is available and provides a greater speed than classic front shelving.
Summarizing the above, it is possible to consider that narrow-aisle storage technology is justified at a very high cost of the warehouse area, which makes it necessary to shorten walkways and “grow” upward or, if necessary, to place a large number of cargo in a limited area (if it is impossible to expand the warehouse boundaries).
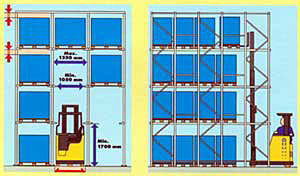
Deep (stuffed) racks Drive-in
 This type of shelving is called differently - deep loading, stuffing, walk-through, and more often, like the English version, Drive-in. The racks are a rigid frame structure of frames forming “corridors” 1350 mm wide, inside of which are placed on horizontal guide pallets with cargo.
This type of shelving is called differently - deep loading, stuffing, walk-through, and more often, like the English version, Drive-in. The racks are a rigid frame structure of frames forming “corridors” 1350 mm wide, inside of which are placed on horizontal guide pallets with cargo.
The design is quite common, providing excellent use of the warehouse area. In fact, stuffed shelving is an advanced rackless storage system, but with better access, reliability and control.
The system is used when storing large volumes of the same type of goods, for which the shelf life is not critical or most importantly - to place the maximum amount of cargo per unit volume of an expensive room with climate control (for example, in refrigerators).
The main and only advantage of stuffed racks is a very high degree of use of warehouse volume. The system has a lot of drawbacks and you should not forget about them. The cost of shelving itself is about 2 times higher than the front; installation is also more expensive due to a more complex design. Despite the large amount of possible storage, it is usually difficult to achieve shelf occupancy by 70% (for comparison, the front - 95%).
It is quite difficult to organize the warehousing of goods of various nomenclatures, most often the principle of one corridor (from the first to the last tier) is observed - one product. It is also problematic to quickly transform the system, for the redistribution of cargo inside the warehouse, it is necessary to do a lot of work.
 If all this is not a serious limitation for your company or if you plan to use several types of racks at the warehouse at the same time, they complement each other - we’ll inform you that classic equipment with slight restrictions is used to work with deep racks.
If all this is not a serious limitation for your company or if you plan to use several types of racks at the warehouse at the same time, they complement each other - we’ll inform you that classic equipment with slight restrictions is used to work with deep racks.
The main requirement is that the machines should already have “corridors” of shelving to ensure passage into the system (see diagram on the left).


