- He wrote in letters. When did the letters appear? (It is believed that already in the 9th century there were books written in “Russian letters.” But they did not reach us, and books of a later period were already written in letters of the Old Slavonic alphabet of the “Cyrillic alphabet.”)
“Why was she called that?” / Answers of the children // The bell rings in audio recordings /
In wide Russia - our mother
The bells are ringing.
Now the brothers saints Cyril and Methodius
For their labors glorified.
Remember Cyril and Methodius,
The glorious brothers of equal apostles
6.In Belarus, in Macedonia,
In Poland, Czech Republic and Slovakia,
They praise the wise brothers in Bulgaria,
In Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia.
7. All nations that write in Cyrillic
What are called since ancient times Slavic,
Praise the feat of the first teachers,
Their Christian enlighteners.
8. Glory to you, brothers, Slavs enlighteners,
Glory to you, church holy fathers,
Glory to you, the truth of Christ’s teachers,
Glory to you, the ABCs of our creators!
9. This visible small book
Spelled alphabet,
Printed speed according to imperial decree
All young children to learn.
1. Cyril and Methodius lived on the border of the state of Byzantium and Slavic lands in the city of Soluni.
2. The younger brother Cyril dreamed of writing books that were understandable to the Slavs, and for this one could come up with Slavic letters.
3. Years have passed. Brothers grew up, learned. But the dream to create the alphabet did not leave his younger brother. He worked hard. And now the alphabet is ready. But coming up is half the battle. Books must be translated from Greek into Slavic so that the Slavs have something to read. It turned out to be difficult, and Cyril alone could not cope. His older brother began to help him.
4. The first book, which is translated into Slavic language - / Gospel /
This event occurred in 863.
5. In Russia, writing came after its baptism, it was in 988
Vladimir was the name of the prince, who took up the baptism of Russia.
6. Since then, the alphabet has changed several times, but until now we use the alphabet, written in ancient times by the brothers enlighteners Cyril and Methodius, for writing.
Leading.
The Slavic alphabet was created on the basis of Greek writing. Strictly speaking - Cyrillic is not the only early Slavic writing. Many scholars believe that the Glagolitic existed even before Cyril. Here is the earliest written language - the Glagolitic alphabet. Look at the icons that marked the letters (Fig. 1). Fig. 1
These icons could be written simple words.
Decipher this word: (Fig. 2).

Vanya: I'm going to the ABC Queen
In my hands - here - I have a bundle
There are signs in it - Slavic symbols
Oh, help me solve them, friends! Read the sentence.
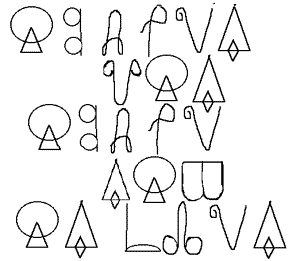
Fig. 3 (“The sun of all suns is the heart”)
- So, on May 24, / what year? / 863 in Bulgaria Cyril and Methodius announced the creation of the alphabet. They tried to make each letter of the first Slavic alphabet simple and clear. They remembered that a person, having barely seen a letter, would immediately want to master the letter. They took part of the letters from the Greek alphabet, and some specially created to convey those sounds that were not in the Greek language. These are letters / cards with Old Slavonic letters: B, F, C, W, U, U, I / - Let's compare Greek and Slavic letters. (Fig. 4).

If you read the name of the first letters of the Greek alphabet, the question arises: why is it so named?
/ alpha + beta / veta / \u003d alphabet /
So today we call the ordinal combination of letters of any language.
And now we read the name of the letters of the Slavic alphabet.
So why the named book by which you learned to read - the ABC?
- Let's look at the first Slavic alphabet - the Cyrillic alphabet.
Beeches - letters, books;
Lead - to know, to know;
Verb - I say the word;
Good is good;
Yes - yes;
Live is life;
Earth– Earth;
How - how;
People are people;
Think - think;
“Why are letters in this order?”
What importance did Cyril and Methodius want to encrypt?
Try to find a trace of the secret words of the alphabet. Compose the text.
(I am a book that knows and says good, is the life of the earth, and how people think.)
That is, the alphabet teaches good, it talks about the life of the earth.
So what's the first letter? - Az.
- No wonder the proverbs were created: "First AZ and BEECH, then science."
Leading. Thank you letters for teaching us beauty, kindness, wisdom. Thanks to the holy brothers Cyril and Methodius for giving us the Slavic alphabet. The Solun brothers are the pride of the entire Slavic people.

"First, yes and beeches, and then science."
Alphabet. ABC.In Greek, the first letter is called alphaand the second - vita. Letters arranged in a specific order were called the alphabet. In the same way the word was formed in Russian aBC.Earlier letter Awas called az, and the letter B – beeches. These obsolete names are preserved in the word alphabet.
T. Andrianova. "A word about words." " Primary School"No. 2 1990.
"ABC. Az. "

"ABC. Beeches. "

"ABC. Lead. ”

"ABC. Verb. "

"ABC. Good."

"ABC. There is."

"ABC. Live. "

"ABC. Land."

"ABC. Izhe. "

"ABC. Kako. "

"ABC. People."

"ABC. Think. "

"ABC. Our."

"ABC. Is he."

"ABC. Peace. "

"ABC. Rtsy. "

"ABC. Word."

"ABC. Firmly."

"ABC. UK. "

"ABC. Firth. "

"ABC. Dick."

"ABC. Tsy. "

"ABC. Worm."

"ABC. Shah. "
![]()
"ABC. SchA. "

"ABC. YU."

"ABC. I AM."

ABC: message to the Slavs.
The Russian Alphabet is not only a set of letters corresponding to sounds, it is also a whole message to the Slavs, deciphered for the first time by our author.
The Russian Alphabet is a unique phenomenon among all known methods of letter writing. It differs from other alphabets not only in the perfect embodiment of the principle of uniqueness of graphic display: one sound - one letter. In the ABC, and only in it, there is content. And the reader will see this for himself now.
First, remember the phrase "Every hunter wants to know where the pheasant sits." It has been known to everyone since childhood and makes it easy to remember the sequence of colors of the rainbow. This is the so-called acrophonic way of remembering: each word of the phrase begins with the same letter as the name of the color: each is red, the hunter is orange, etc.
However, acrophonic memorization is far from a children's game. For example, after the invention of S. Morse in 1838, a code for telegraphic communications arose a problem with the mass training of telegraph operators. Learning Morse code quickly was harder than the multiplication table. A solution was found - for the convenience of remembering, each Morse sign was associated with a word starting with the letter that the character conveys: for example, a dash-dot that conveys "a" is called "watermelon".
Acrophonia helps to quickly remember the ABC and thereby maximizes its rapid spread.
Among the main European alphabets, only three are more or less endowed with acrophonicity: Greek, Hebrew, and Cyrillic (\u003d Glagolitic). The Latin alphabet does not have this property, so it could appear only on the basis of the already widespread written language, when acrophony is no longer essential.
In the Greek alphabet, the remnants of acrophonia can be traced in the names of 14 of 27 letters: alpha, beta (more correctly - vita), gamma, etc. However, these words mean nothing in the Greek language, they are slightly distorted derivatives of the Hebrew words alef (bull), bet (house), gimel (camel), etc. Hebrew still fully maintains acrophony, which, by the way, contributes a lot fast learning immigrants in Israel. Comparison on the grounds of acrophonicity directly indicates that the Greeks borrowed part of the Hebrew script.
The Orthodox Alphabet is also completely acrophonic, but in one respect it differs significantly from Hebrew. In Hebrew, the names of letters are nouns in the singular and nominative case, and among the names of 29 letters of the Slavic alphabet at least 7 words are verbs (see table). Of these, four are in the imperative mood: two in the singular (rts, tsy) and two in the plural (think, live), one verb in indefinite form (s), one in the 3rd person singular (is) and one in past tense - “lead.” (Note: in "ancient" Hebrew, the concept of verb none at all). Moreover: among the names of letters there are pronouns (kako, shta), and adverbs (firmly, zelo), and nouns in the plural (people, beeches), as in ordinary speech.
Comparative analysis of the Pre-Slavic alphabet, the Greek alphabet, Hebrew and Latin
Letters in brackets are taken that are not in their alphabetical ordinal places. Letters transmitting other sounds or not transmitting sounds are marked in italics. Numerical values \u200b\u200bof Church Slavonic and Greek letters are also given.
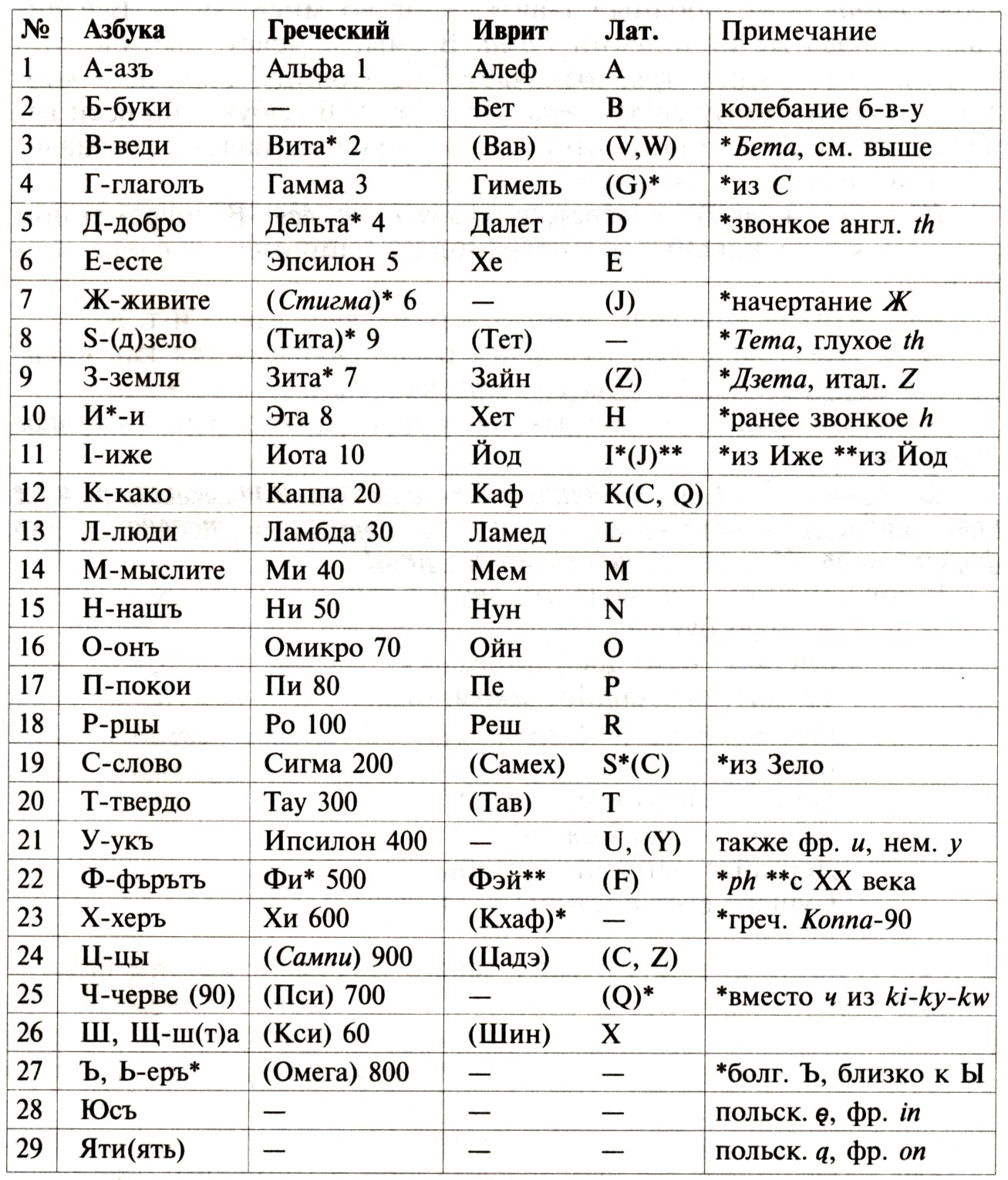
In normal coherent speech, one verb falls on average to three other parts of speech. In the names of the letters of the Pre-Slavic Alphabet, it is such a frequency of the verb that directly indicates the coherent character of the alphabet names.
Thus, the Pre-Slavic Alphabet is a Message - a set of coding phrases that allow each sound of the language system to give an unambiguous graphic correspondence - that is, a letter. In this case, the lettering systems for transmitting the same sound system can be different, for example, Cyrillic \u003d Glagolitic for the Proto-Slavic language, Cyrillic \u003d Latin for the modern Serbo-Croatian language, three equal systems of medieval Georgian writing, known from history, etc.
And now we will read the Message contained in the Pre-Slavic ABC.
Consider the first three letters of the alphabet - Az, Buki, Vedi.
Az - "I am".
Beeches (beech) - letters, letters.
Lead(vede) - “knew”, the perfect past tense from “vediti” - to know, to know.
Combining the acrophonic names of the first three letters of the ABC, we get the following phrase: Az buki vede
“I know the letters.”
All subsequent letters of the ABC are combined into phrases:
Verb - “word”, and not only spoken, but also written.
Good - "wealth, acquired wealth."
there is (nat) - 3rd l. units hours from the verb "to be."
Verb good nat
: a word is an asset.
Live(instead of the second “and” the letter “yat” was written earlier, you pronounced live) - imperative mood, plural of “live” - “live in labor, and not vegetate”.
Zelo (the combination of dz \u003d voiced c was conveyed) - "assiduously, with zeal."
Land- “planet Earth and its inhabitants, earthlings».
AND- union “and”.
Like - "those that they are."
Kako - “like,” “like.”
People - "sentient beings."
Live zealously, the earth and others like you: live, working hard, earthlings, and as befits people.
Think (it was written with the letter "yat", pronounced "thought", as well as "live") - the imperative mood, pl. h. from "think, comprehend the mind."
Our - "ours" in the usual sense.
He - “one” in the meaning of “single, single”.
Chambers (peace) - “the basis (of the universe)”. Wed “Rest” - “be based on ...”
Think of our peace: comprehend our universe.
Rtsy(rtsi) - imperative: "speak, speak, read aloud." Wed "Speech".
Word - "transmitting knowledge."
Firmly - "confidently, confidently."
Rtsy word is firmly - "carry knowledge with conviction."
Uk - the basis of knowledge, doctrine. Wed science, learn, skill, custom.
Fert f (b) Ryt- "fertilizes." The ABC recorded the difference in the sounds “p” and “f”, as well as their sonorous analogs “b” and “c”. in the Middle Ages, the South Europeans who pronounced “f” instead of “p” were called “jerks” in Russia precisely because of the peculiarities of speech: this, for example, distinguished the southern Franks from the northern Prussians, the Thracians from the Persians, etc.
Her - "divine, given from above." Wed him. Herr (lord, God), Greek “Hiero” (divine), English hero (hero), as well as the Russian name of God - Horse.
Uk fier Her: knowledge fertilizes the Almighty, knowledge is a gift of God.
Tsy(qi, tti) - “sharpen, penetrate, penetrate, dare”.
Worm (to the worm) - "he who sharpens, penetrates."
W (t) a(W, SH) - “what” in the meaning “to”.
B, b (er / yer, yr) - are variants of one letter, meaning an indefinite short vowel, close to uh.
The rumbling sound “p” is pronounced with the obligatory initial aspiration (initial “b”) and echo (final “b”). The word "yr", apparently, meant the existing, eternal, innermost, space-time, inaccessible to the human mind, the lamp, the Sun. In all likelihood, “bp” is one of the most ancient words of modern civilization, cf. Egyptian Ra - The Sun, God.
The word "time" itself contains the same root, since the initial "c" developed precisely from "b". Many primordially Russian words contain this root, for example: morning - “from the Sun” (the root ut - from there, there); evening (century p) - “century Raexpiring time of the sun. "
In the sense of “space, the Universe,” Russian originates from the same root "frame". The word "paradise" means: "many suns" \u003d "abode of the gods (God Ra)." Gypsy self-name "Rum, rum" - “free”, “God is in me”, “I am the Universe”, hence the Indian Frame. In the sense of “light, luminary, source of light”: cry "Hooray!" means “to the sun!” yarcue - “like sunshine”, “ raarc ", etc. In the ABC, in all probability, the word" bp (a) "is in the genitive case with the meaning of" Existing ".
Yus (us small) - “light, old Russian clear". In modern Russian, the root "Clear" preserved, for example, in the word "clear."
Yat(yati) - “to comprehend, to have). Wed ex to ya, take to ya etc.
“Hey, worm, shta yus yati!”
stands for “Dare, sharpen, the worm, to understand the Light of Jehovah!”
The combination of the above phrases is alphabet Message:
Az books. The verb is good nat. Live zelo, the earth, and, like any other people, think our chambers. Rtsy word is firmly - uk fart. Tsy, worm, shta yra yus yati!
In a modern translation, it sounds like this:
I know the letters:
writing is an asset.
Work hard, earthlings,
as befits intelligent people -
comprehend the universe!
Carry the word with conviction:
knowledge is a gift of God!
Dare, delve into
Realize the light to comprehend!
Yaroslav Kesler. "Alphabet: a message to the Slavs." Reading "Miracles and Adventures." Moscow, "Desnitsa". 2002 year.
"ABC. Yer Yer. Yer Yat. E. Yus. From. Xi. Psi. Fita. Izhitsa. "

As I have already mentioned, the Alphabet was given to the Lords immediately, brought from the Moon by Heavenly intercessors - Slovians, and did not develop, as in the theories of most of the scientists of Thera. Over time, he was perverted, poher ("Herr" - the Lord in German) God's slaves and his avatars. While the giants were alive, they periodically restored it, almost to modern look. The servants of God mutilated and divided him, branched into pseudo directions and dead ends. The main line of the involution and decay of the alphabet (and language), not counting the side branches, looks something like this: Slovenian - Slavic - Hebrew - Ancient Greek (Judeo-Hellenic) - Latin and so on. With the advent of Christianity, God's work began to boil with new force to divide the remnants of spiritual unity and culture into information principalities and clans. So the gods broke their tongues and divided people to rule over the World. Such tools were: the Orthodox church alphabet, the ligature of the Koran, Sanskrit, Hebrew, Latin and many other alphabets of the torn World. The word "alphabet" in transit comes from the Judeo-Hellenic "Aleph and Vita", Aleph - Bull (alpha) - God, Vita - life. And the name of the Russian alphabet, by the name of the first letters: Az - Ass (God). (“I am,” “I am God,” says the avatar of God, the king says so.) For example: the word Sanskrit (not so ancient), in Spanish “San Escripto” means “Holy Scripture, so there’s no need to fool the little ones about Sanskrit antiquity and exclusivity is a piece from a common, once a single group of languages. Words (over 100 words) from Sanskrit and even whole phrases are identical to the modern Russian language. (For example, the phrase “WILL STAND BY THE HAND” in Sanskrit and Russian sounds the same!). Also, many almost identical words that are similar in sound and meaning are found in any other languages \u200b\u200band dialects of the world.
The Indian Vedas, with a description of wars against gigantic non-Aryan peoples, are for the most part genuine, simply very distorted narratives of the affairs of bygone days. These are stories distorted by the "national" Hindu flavor, borrowed from the libraries of the old world. Information was exported to the East, in Shambhala, to create various world religions, pseudo teachings on the discipline of the body and the purification of the body and soul. The great spiritual godfathers of the East propose to do this. different ways, for example, with the help of the Kama Sutra, bestiality or ablution in the stinky, infested with infectious and dead bodies of the Ganges (liquid cemetery in India). True, some elements of yoga, in spite of the attention of the “great confessors”, have preserved Ancient practicality, everything else is more “spiritual” garbage in a colorful and odorous package.
CREATION OF THE “OWN” DEVIL OF LITERATURE HAS POSSIBILITY OF THE SERVANTS OF THE LORD DEVIL TO REWRITE HISTORY, THINK AND WRITE YOUR VERSION OF “CREATING PEACE”, BLEND LUMBERS, WITHOUT RETAINING.
B. Pyatibrat. The Deep Book.
Lesson Objectives:
- To give an idea of \u200b\u200bthe history of development and the formation of the Russian language.
- To highlight the problems associated with the current state of the Russian language.
- To instill a love of the native language.
Decor:presentation (slide show about the history of the development and formation of the Russian language).
During the classes
A student performs a Russian folk song "How do I go to the fast river."
Teacher: "Rus" - short - in one syllable of everything! - And such a spacious and mysterious word! - Russia!
It came from hoary antiquity and forever remained with us. What does it mean? The word "Rus" has many meanings, like many tributaries of the great river. Russia. Russians. Russians. Russia. But there are also related words: channel, mermaid, dew, dewdrop. So, Russia is a country where there are many rivers and lakes, and Russian is a man living near the water.
So we went with you on an exciting journey in which you will learn a lot of new and interesting things about your native language. And our journey will be called: "First AZ and BEECH, then all sciences." You must have heard this proverb more than once. Its meaning is this: first learn the language, then proceed to the sciences.
Assistant student: But what are the words "az" and "beeches", what do they mean and where did they come from ?! To understand this, we will get acquainted with the history of writing and the origin of the Russian language.
In ancient times, people, instead of writing, painted. The remains of the picturesque letters are still preserved in our everyday life. Think about where you can see a picture letter? (Slide 2)
Teacher: Let us turn to our sources. Russian language belongs to the Slavic group of languages. Related to him are the East Slavic languages \u200b\u200b- Ukrainian and Belarusian; Western Slavic - Polish, Kashubian, Czech, Slovak, Puddle; South Slavic - Bulgarian, Macedonian, Serbian, Croatian, Slovenian. These languages \u200b\u200bhave a lot in common, but there are significant differences. We listen to the dialogue of two Slavs: Bulgarian and Russian
The scene.
When our soldier entered into a conversation with the Bulgarian, they, sweetly smiling at each other, all the time tried to moderate the pace of the conversation.
Nice man, ”the Russian coaxed,“ do not speak so fast, speak more slowly! ”
It’s me who they are to my friend, don’t say so borzo, speak and it’s important! - answered the Bulgarian.
Speak more slowly, not part - this is understandable. But what am I to amuse you with, so that it is also fun, i.e., sparingly. The first half of this sentence did not bother any of us: “takA borzo” means “so fast”. Naturally, the “greyhound horse” in Russian is “fast horse” ... But the unexpected word “bavno” was thought-provoking ... - how do they say - brotherly language, the closest? But it turns out the opposite. We have "funny" - fun, funny, and they have "bawo" - slowly.
Why do you think this happens? (Mini discussion.)
Assistant student: By the 5th-6th centuries Among the Slavs, three groups were distinguished: southern, western, and eastern. (Slide 3)
By the XII century, Kievan Rus was the largest state in Europe, on its territory formed the Old Russian nationality. Subsequently, on its basis the Russian, Ukrainian and Belarusian nationalities will be formed.
Teacher: The next stage of our journey is the emergence of writing in Russia. Remember when writing appeared in Russia? What historical event is it associated with? (988, adoption of Christianity in Russia.) (Slide 4) Musical background: A. Bortnyansky “Lord, have mercy.”
Assistant student: The birth of the Slavic alphabet is inseparable from the names of Constantine (Cyril) and Methodius, "brothers from Soluni." In the X century, the Greek monk Cyril created the alphabet for the southern Slavs, using the Greek alphabet for this. This alphabet, named after its inventor, the Cyrillic alphabet, began to be used by the Eastern Slavs, the ancestors of the present Russians, Belarusians, and Ukrainians. In the Slavic alphabet, in order to facilitate memorization, letters were called by the words: AZ, BEECHES, LEAD, VERB, GOOD, IS, etc., which in Russian means: "I know the letters (I know), I say - there is good." The ABC was a solid text of a moralizing character.
Teacher: Guys, how many of you know which letter became the heroine of phraseology? What does she mean? (To register Izhitsa - to someone to make an suggestion.) (Slide 5)
Scene "ABC".
At school. There is a long table on the stage. At the table on one side are several students. At the head of the table "Master" is a teacher. He has a rod in his hand. The rods hang on the wall by the window. (Slide 6)
Master (holding a folder in its cover, on one side of which is coarsely written “AZ”, and on the other “BEECHES”):
BOOKS YOUR WELLS KEEP. Do not bend the sheets in vain. Anyone who doesn’t protect the book doesn’t guard his soul. If you abide in my orders, you will never be beaten from me. Set your ear to attention, sit quietly like a fly. Yes, do not laugh and do not look with your eyes, as though you were being plagued, otherwise I would write you an Izhitsa. (Shows the cover with the letter "AZ".) What is the name of this visible sign?
Boys: AZ!
Master (turning over the folder): And this visible sign?
Boys: Beeches!
Master: Well, loudly: beeches and az are saying "BA!"
Boys: Beeches and az say "BA!"
(Boy 1 yawns in full mouth. He begins to fall asleep. A neighbor pinches him when he bites his nose. Boy 1 jumps and shoves his neighbor in the side.)
Master: I hear the noise is not useful! And for this, you will be weeping tearful. Whoever does not learn the lesson will not receive a free exit from school. Who rests in evil, he lies on the school goat on the school.
Boy 1:And where he? (The master gets up, takes both kids by the ears and leads to the bench.)
Master: Well get up, take a break! Now pray and go home for dinner, then come back to study again!
Teacher:1564 - what is the date in the history of the Russian language? (The first book “Apostle” was printed - the beginning of book printing in Russia.)
(Slide 7) Musical background: M. Mussorgsky “Chorus of Girls (Great)” from the opera “Khovanshchina”.
- Who was the first book printer? (Ivan Fedorov, and in Belarus and Lithuania was Francis Skorin. The first book was called “The Bible of Russian”, which he published in 1517.)
- In 1564, the printing press opened. And what modern synonym can replace this word? (Typography.)
- Why did Ivan Fedorov have many enemies? (The printing yard replaced the work of hundreds of scribes.)
- Why are printed books better than handwritten? (An increase in the speed of book production, books have become cheaper, fewer errors.)
- Why were books needed in those days? (To teach children, to celebrate church service, to transfer knowledge from generation to generation.)
Reforms of the Russian language.
Throughout its development, the Russian language has undergone changes several times. One of the reformers of the Russian language was M.V. Lomonosov. (Slide 8)
Assistant student: He created “Russian Grammar”, the first ordered rules of Russian spelling, he wrote “A Letter on the Rules of Russian Poem”, in which he derived the theory of three “calm”. Can you tell what this theory was? (High, medium and low styles were created.)
In the 19th century, Nikolai Mikhailovich Karamzin introduced a new letter into the Russian alphabet. What was that letter? (Letter Y.)
Another reform was carried out in the twentieth century, in 1918. The extra letters YAT, IZHITSA, FITA and Kommersant at the end of the words were eliminated, which made it easier to learn the alphabet.
Aliens words.
Teacher: Talk about alien words.
The student reads a poem:
We are pretty secular people
Recognize Turkish
Italian, Danish, Swedish,
And the Chinese recognize
Both English and French,
But in the native land in Russian
We write, think, sing
Teacher:The Russian language in different eras perceived words from other languages, some alien words penetrated the Russian language for so long that they became very familiar and now seem to us to be our own, native Russian.
Guys, what do you think are the reasons for borrowing? (Cultural and historical ties, trade ties.)
What do you think, when and in connection with which were borrowed words from Greek, Latin, German, Dutch, French and english languages? In your answer, rely on a knowledge of history. (Slide 10)
| LANGUAGES | ||||
| Greek | Latin | German and Dutch | French | English |
| Apostle. Demon. Gospel. Department. Library. Grammar. School. Notebook. Drama. Theater. The bathhouse. Sugar. Cucumber. Cypress. Tape. | Republic. Revolution. Operation. Station. Pencil case. | Accountant. Locksmith. Fair. Workbench. Fleet. Anchor. | Opera. Scene. Ballet. Poster. Producer. Vest. Hood. Veil. Coat. Parquet. Sidewalk. Shade. Service. | Railway station. Rail. Tram. Tractor. Harvester. Tank. Football. Start. Club. The meeting. Jumper. Plaid. |
But do not you think that we sometimes spoil our language? We use foreign words unnecessarily, wrong? (Student responses, mini-discussion.)
Why say "defects" when you can say "flaws" or "flaws." And at the same time, is there any point in “inventing” the original Russian synonym for the word “computer”?
Conclusion of the teacher: each style of speech has a certain vocabulary. You need to know when to use it.
Modern Russian language
Today we are talking about the richness, diversity of the Russian language. And what times is the modern Russian language going through today?
Some believe that our language has fallen into decay, someone says that such situations when the level of literacy drops sharply have already been in history. Language is always a reflection of the life of human society. There is nothing in it that is not in man. The fate of the tongue is entirely in the hands of people. The position of the language is both a social diagnosis and an indicator of a person’s internal culture.
The problem of the modern Russian language lies, firstly, in the fact that a lot of jargonisms, borrowings, which are not always justified, began to get into the language. Let us trace this as an example of a parody of a fairy tale.
Tale of Little Red Riding Hood (scene).
All the way, with terrible force hanging out in the woods, breaking away at 100, the Gray Wolf stuck to a cool chick in a stunning red hat from Dolce & Gabana. She immediately entered that the Gray Wolf is a sucker, a loser and began to hang noodles on his ears about a frail club, i.e. sick grandmother.
Listen baby, take the pill. And if you want, pussy, buy yourself a whiskey, ”said the Gray Wolf,“ this is not a fountain, millet is not for life. ”
Otpad, - said Little Red Riding Hood. Be healthy, do not sneeze! And then you glue the flippers and hiccup.
Such a retelling of the tale is a vivid illustration of speech containing jargon, vulgarism. In recent years, the Russian language has turned into an unsounding mixture of foul language, gangster jargon, distorted "Americanisms" and illiterate Russian words. People who continue to speak “archaic” Russian often do not understand their compatriots. Now you will not hear the combination “in life”, but for some reason only “in life”. The previously used verb “count” has become a kind of word - a bunch. But the other Russian verb “put” disappeared altogether and was almost replaced by the ugly “lay down”.
This is manifested both in everyday speech and in professional. Special “dialects” appear, and often employees of neighboring departments of the same company speak different languages. For example, one of the most common expressions in the fashion business is “create a bow” (“look” is an image; we are talking about choosing clothes, and even “total bow” is to be worn one brand from head to toe) of a man who is wearing shoes not just in the clothes of one brand, but also from the collection of one season, they will call it “fashion victim” - fashion victim - fashion victim.
One more problem - we began to read less. According to the survey on the number and genres of readable literature - 37% of respondents do not read books at all. And those who read, choose the "easy" genres - detective story, "love" novel, preferring them to the classics.
Methods of obtaining information are changing. In the media, on the Internet, far from all the wealth of the Russian language is used. The lexical stock of a person is noticeably thinner. Many suffer from this, because cannot pick up words to express a thought.
Scientists see a change in the situation in the study of the Russian language, starting from kindergarten and ending with high school.
Linguistic scientists propose to establish a national holiday in Russia - the Day of the Russian Language, and celebrate it on the birthday of A.S. Pushkin.
Russian is the mother tongue of 288 million people in more than 15 countries. We, the native speakers of the Russian language, a lot. So let us be united in our desire to preserve our national treasure - the modern Russian literary language.
Our linguistic journey ends. (Slide 10) Musical background: V. Zakharchenko “Russian Orthodox”.
Yes, it is important to know several languages \u200b\u200bnowadays, but it is best to know your native language and strive to enrich your speech. As M.V. used to say Lomonosov, the Russian language combines "the splendor of Ishpan, the liveliness of French, the strength of German, the tenderness of Italian, moreover, the richness and strong brevity of Greek and Latin in the images ..."
So let us be proud of our language and love it.
She speaks soundlessly
But it’s clear and not boring.
You talk more often with her -
You’ll become four times smarter.
(Book)
That's right, and today is our class hourOrthodox Book Day . And how did writing appear in Russia? To whom should we say thanks for using the written speech?
1 reader Look back at our ancestors
On the heroes of past years.
Remember them with a kind word
Glory to them severe fighters!
Glory to our side!
Glory to Russian antiquity!
And about this old
I'll start telling
So that people can know
About the affairs of the native land ...
2 reader In the monastery cell narrow
In the four blank walls, A monk wrote down the earth about Old Russian Life ...
Indeed, the book was created for our happiness and salvation.
A word ... A sound that lives for a split second and disappears into space. Maybe there’s nothing to talk about. But the word is a gift of God. After all, in the beginning was the Word. And the first word was - God. The Word of God was embodied in Slavic speech thanks to the solunky brothers Cyril and Methodius, the creators of the Church Slavonic language. This word of God is the Book of Books, the Bible, otherwise the Gospel. Pupils learned the Slavic alphabet from the ABC book: az, beeches, lead, verb, good. All schools were at the temple, and teachers were church ministers.
Wake up early
Wash your face white
Get ready for God's church
Begin the alphabet!
Many years have passed since then. People learned to print not only church books, but also popular novels, magazines, and various press. But lest we read, we must not desecrate our speech, which Cyril and Methodius created in order to write down the very first and main book - the Bible. Before the advent of typography, it was rewritten many times, and not a single mistake was made. We start our story with this book.
"The Bible or the Gospel."
There are many Orthodox books in my home library. But the most important of them is the Bible. Since ancient times it was called the Book of Books. It consists of two parts: the Old and New Testaments. The New Testament tells about the life of Jesus Christ. The Four Apostles wrote the New Testament or Gospel: Matthew, Mark, Luke and John.
With love for his neighbors a flame, The people humbly he taught; He subordinated all the laws of Moses of Love to the law. He professes forgiveness; He orders that evil be paid with good; There is an unearthly power in it. Aiming ailment, treating flour, Everywhere he was a savior. And he extended a good hand to everyone, And he did not condemn anyone.
IN863 Slavic alphabet was created in the year.This year is considered the year of birth of the Slavic alphabet. Slavic alphabet existed in two versions:glagolitic – from the verb - “speech” andcyrillic .
In the first Slavic alphabet there were 40 letters. She was called"Glagolitic" and her brothers created it on the basis of three Christian symbols - a cross, circle and triangle, independently of other alphabets.
Later, in Bulgaria, the students of Cyril and Methodius invented the second and main Slavic alphabet -cyrillic alphabet Cyril. Each letter of the Cyrillic alphabet was special. She had the name: A - az, B - beeches, C - lead, G - verb, D - good, E - eat, F - live, 3 - green, earth, L-people, M - think, P - peace, R - rtsy, speech, C - word, T - firmly ... In addition, the letters could also indicate the numbers: "az" - 1, "lead" - 2, "verb" - 3.
The creators of the alphabet tried to make the letters simple, clear, soft in writing. Cyrillic is still considered one of the most convenient writing systems. And the names of Cyril and Methodius, "the first teachers of Slovenian", became a symbol of spiritual achievement.
Russian alphabet is a completely unique phenomenon among all the known methods of letter writing. In the alphabet, and only in it, there is content.
The creators of the Slavic alphabet Cyril and Methodius did not accidentally give the names of the letters. They wanted the alphabet to sound meaningful, affirming the value of words and thoughts.
Using the Old Slavonic language, the scribes brought it closer to their native languages \u200b\u200b- Russian, Serbian, Bulgarian. This version of Old Slavonic is now called Church Slavonic.
SLAVIC PEOPLE thanks the Primary teachers of Slovenia.
Monuments to Cyril and Methodius are in Croatia, Bulgaria, In Russia.
On the day of Slavic writing and culture, a prayer service is held on Slavyanskaya Square in Moscow.
In 2004, Samara became the all-Russian center for the Days of Slavic Writing and Culture.
In wide Russia - our mother
The bells are ringing.
Now the brothers saints Cyril and Methodius
For their labors glorified.
Remember Cyril with Methodius,
The brothers are glorious, equally apostles,
In Belarus, Macedonia,
In Poland, Czech Republic and Slovakia.
They praise the wise brothers in Bulgaria,
In Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia.
All the nations that write in Cyrillic
What are called since ancient times Slavic
Praise the feat of the first teachers,
Their Christian enlighteners.
Once upon a time, when the history of a great Russian power was just beginning, “it” was very expensive. She alone could be exchanged for a herd of horses, a herd of cows, for sable fur coats. And the point here is not the jewelry in which the beauty and the clever were dressed up.
And she walked only in embossed leather, in pearls and precious stones! Gold and silver clasps adorned her outfit! Admiring her, people said: “Light, you are ours!” ... What kind of wonder is this? This is Her Majesty - BOOK.
She has preserved to us the Word of God and the traditions of distant years.
A deep bow and thanks to Cyril and Methodius! Our respect is for Orthodox books that teach us to be kind, fair, patient and loving, books whose authors dreamed that the world would become cleaner and brighter. We will remember this always and everywhere.


