The verb “to be”
“How much of this verb” is for sure, because without him anywhere in english language. These are the basics of grammar.
The very first thing you need to know:
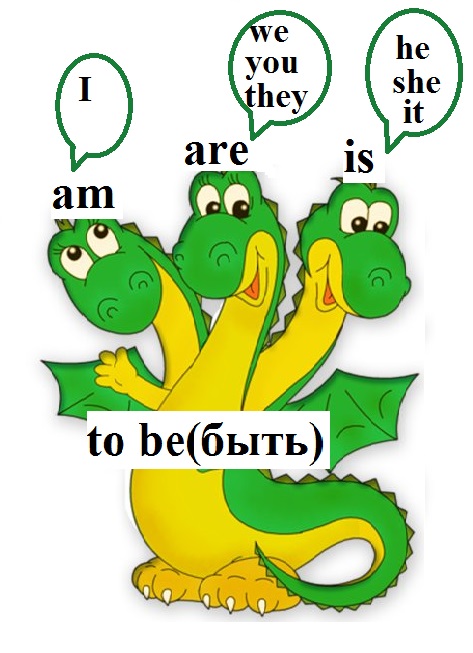
In the present tense, the verb “to be” has 3 varieties: is, am, are.
- I - I am
- He she - He, she is
- They, we, you (you) - They, we, you are
IN negative offers to is, am, are add the negation NOT, and we get:
- I - I am not
- He she - He, she is not
- They, we, you (you) - They, we, you are not
IN interrogative sentences the verb “to be” (is, am, are) is moved to the 1st place and we get:
- I - am I?
- He she - Is he, she?
- They, we, you (you) – Are they, we, you?
Exercises for the verb TO BE
Let's fix it by doing a little exercise. It is lightweight, suitable for those who are just starting to learn English. Insert the verb “to be” in the correct form:
- My friend ... kind and nice.
- These monkeys ... really funny!
- ... you fond of reading?
- She ... not bad and naughty!
- I ... 16.
- My sister ... very beautiful and clever.
- We ... friends forever!
- My parents ... not lazy, they work very hard.
- I ... a little bit angry now.
- My kittens ... so nice.
Here is such a small exercise in the English verb “to be”.
Exercise Answers
Now check yourself - answers:
1. is 2. are 3. Are 4. is 5. am 6. is 7. are 8. are 9. am 10. are
Have you had any difficulties? If so, read the exercise comments:
- My friend - my friend, you can replace the pronoun he, after he and she you need to put the verb IS.
- These monkeys - these monkeys can be replaced by they. After they, we, you - the verb are.
- Suggestion is a question. We put the verb first. You pronoun - set are.
- After the pronoun she put is.
- My sister - my sister, replace with she, after he and she you need to put the verb IS.
- After the pronoun we go are.
- My parents - my parents can be replaced by they. After they, we, you - the verb are.
- After the pronoun I set am.
- My kittens - my kittens can be replaced by they. After they, we, you - the verb are.
Hopefully the English verb “to be” changes you have learned in EXCELLENT!
The cunning verb to be loves to wear masks. It’s like a bunch, then like an auxiliary. Yes, and in every time has its own forms. How to expose it?
Easy! First you need to thoroughly study the rule about the use of the verb to be in English, its conjugation in persons at all times. All this can be found in the article “Verb to be in English”. Well, then take it to clean water. After all, you don’t want to think in what function it is used here, what does it mean? So you need to fill your hand in exercises about the verb to be.
What stages to go through to be fully explored?
Before moving on to all forms and functions to be, practice its use like a verb-bunch separately for all times. For example, in the present tense it has the forms is, am, are. In the past - was / were, and in the future - will be / shall be. Remember that for the formation of negatives and questions, no auxiliary verbs are required in this case.
I am the first year student. “I'm a freshman.”
He is my best friend. - He is my best friend.
We are not (aren’t) there now. “We are not there right now.”
Are you at home? - You are at home?
We were in this museum yesterday. - We were at this museum yesterday.
I was here the other day. “I was here the other day.”
He wasn’t at school. - He was not at school.
She will be a doctor. - She will be a doctor.
Now let's look at its use, as auxiliary verb. So, to be used in times continuous Active in Present perfect Continous Active used 3rd form - been which is also auxiliary. Exercises for to be will help facilitate understanding.
He is playing football now. - He plays football now.
I am not writing a composition, I am reading a book. “I am not writing an essay; I am reading a book.”
We were sleeping at 6 yesterday. - Yesterday at six we slept.
I will be taking a shower at 5 tomorrow. “Tomorrow at five I will take a shower.”
He has been walking for 3 hours. - He walked for 3 hours.
I have been cleaning the flat for 5 hours. - I cleaned the apartment for five hours.
But there are still moments. Passive voice uses to be as an auxiliary verb: simple group, Present continuous Passive - is / am are + being, Past Continuous Passive - was / were + being, Perfect Passive - been. Yes, note that Continuous Passive uses two forms at the same time: 1st (is, am, are) and fourth (being). Let's look at examples to make it clearer what you are talking about.
The flat hasn’t been cleaned yet. - The apartment has not yet been cleaned.
We had been invited to the wedding party before we knew about the accident. - We were invited to a wedding before we heard about the accident.
The letter is being written now. - The letter is being written.
Are the potatoes and tomatoes grown here? - Do you grow potatoes and tomatoes here?
The children were being watched all the time they were there. - Children were watched all the time while they were there.
We were taken to London by a friend of us. “One of our friends took us to London.”
When you understand all three stages, you can move on to the study of stable expressions. Exercises for the verb to be will help you remember more stable phrases.
Well? More or less clear? Can we pass the to be conjugation test in English?
Exercises
1. Put the appropriate form to be
- My uncle ... a director of the large company. He ... often on a business trip. Yesterday he ... in France. Tomorrow he ... in England. Last week he ... in Spain. Now he ... at home with his family. His daughters ... so much exited.
- The students ... at the hostel now? My sister ... not at work next month. Where ... your mother now? He ... not a pupil 20 years ago. We ... at this place last week.
Answers:
is / is / was / will be / was / is are
Are / will not be / is / was not / were
2. Put the appropriate form to be according to the time indicated in parentheses.
- Her car broke down yesterday while she ... driving to work. (Past Continuous).
- Who ... speaking there? (Present Continuous)
- We ... flying over Paris at this time tomorrow (Future Continuous).
- She has ... doing her homework since morning (Present Perfect Continuous).
- I had ... working in the garden before he came (Past Perfect Continuous).
- The flex .. grown in the fields (Present Simple Passive).
- The door ... painted yesterday ( Past simple Passive).
- When I came into the laboratory, the lab had already ... tested the device (Past Perfect Passive).
- The bridge ... repaired now (Present Continuous Passive).
- The photos ... shown the whole evening (Past Continuous Passive)
- will be
- is being
- were being
Fill in the gaps as in the example
| Negative short form |
|||
| We are students. | We’re students. | We are not students. | We aren’t students. |
| He is from Spain. | |||
| You are a singer. | |||
| It is a picture. | |||
| They are actors. | |||
| She is in London. | |||
| I am a businessman. | |||
Complete what Brenda says about herself. Use am, is, are. Make up the same story about yourself
My name __________________ Brenda Foster. I __________________ ten years old and I __________________ in the fifth form. My birthday _________________ on the fifth of May. I __________________ from Santa Monica, California, USA. I __________________ American. My phone number __________________ 235-456-789. I live at 16 Park Street. My post code __________________ LA 30 SM. I’ve got a sister and a brother. Their names __________________ Gina and Paul. Gina __________________ 16 years old and Paul _______________ only three. I’ve also got a dog. His name __________________ Spot. My mum __________________ a doctor. She works at a hospital. My dad ____________________ a driver. He works in Los Angeles. We _________________ all friendly in our family.
Add ponytails to 1 to 6 sentences. Make all offers negative. Add Ponytails to 7 - 11 Negative Sentences
1. My friend is naughty.
2. My granny is kind.
3. My granddad is clever.
4. My teachers are funny.
5. My uncle is a driver.
6. My parents are doctors.
7. My mum is a shop-assistant.
8. Jenny is at the party.
9. You are happy.
10. Your friend is at school.
11. Your teachers are sad.
Answer the questions
1. Are you a student? 2. He is at home, is not he? 3. She is not busy, is she? 4. Are the children at school? 5. They are at the lesson now, are not they? 6. Tommy and Billy are not babies, are they? 7. Are the spoons on the table? 8. Your friend is a good student, is not he? 9. The weather is not fine today, is it? 10. You are interested in music, are not you? 11. Are your grandparents old?
Complete the sentences with "to be"
1. I _____ a girl. 2. My father_____ at work. 3. Alex and Dino _____ my cats. 4. Alex _____ in the garden. 5. Dino _____ on the floor. 6. My red pencil _____ on the floor, too. 7. The other pencils _____ in my pencil case. 8. My mother _____ in the living room. 9. Eli and Rafa _____ good friends. 10. They _____ good at tennis. 11. _____ they in Amsterdam this week?
1. You are our best friend. 2. He is an excellent driver. 3. Ann is a perfect housewife. 4. My friend and I are drivers. 5. I am busy. 6. She is responsible for children. 7. These things are dangerous. 8. The weather is nice. 9. This shirt is old. 10. She is happy. 11. His computer is old.
Insert the verbtobe in the right form. Add « tails» tosuggestions 1, 5, 6, 8.
1. My telephone ___________________ broken yesterday. 2. He _________________ a dentist. 3. ______________________ you in Paris? Yes, I _________________. 4. We ___________________ late for work last Tuesday. 5. My shoes __________________ not too tight. 6. Her hair _________________ not blond. 7. __________________ are you tired after work? No, I _________________ not. 8. The fridge _______________ not switched off an hour ago. 9. We ___________________ not busy last week. 10. __________________ the books boring? Yes, they __________________. 11. _________________ your daughter an economist? No, she _________________ not.
Answer the questions
Translate into English
1. Where are the students? They are in the UK. 2. What is dirty? His shirt. 3. I am beautiful. 4. Tom is smart, right? Yes. 5. Your birthday is not September 9, is it? Not. 6. Are the crocodiles green? Yes. 7. He is not from the UK. 8. Where is your dad? At home. 9. Who is the engineer? His brother. 10. She is not a student. 11. Her sister is not a teacher, is she? Not.
Answeron thethe questions
1. Where are you? 2. Who is an engineer? 3. His parents are at work, are not they? 4. Jeff is not crazy, is he? 5. Is this apple red? 6. Where is Harry? 7. Who is angry? 8. Her love is true, is not it? 9. Fred is not nice, is he? 10. Are her friends strong and healthy? 11. Where are crocodiles?
Make the necessary changes so that the offers inPresentSimple became offers inPastSimple, and the sentences inPastSimple became offers inPresentSimple
1. She is a doctor. 2. Bob is an engineer, is not he? Yes, he is. 3. We are not managers. 4. Helen is not a nurse, is she? No, she is not. 5. Is Denis a programmer? Yes, he is. 6. Who was a secretary last year? Olga was. 7. They were economists five years ago. 8. The weather was nice yesterday, was not it? No, it was not. 9. I was not tired last week. 10. Her shoes were not very dirty five minutes ago, were they? Yes, they were. 11. Were shops open last Saturday? No, they were not.
Fill in the gaps with the verbtobe inPastSimple. Translateany 6 suggestions
1. I __________________ at the party last Saturday. 2. You ___________________ in Kongo in 2014. 3. He __________________ in the local gym last week. 4. She __________________ at school three minutes ago. 5. We ___________________ happy last year. 6. They ___________________ tired five hours ago. 7. Jenny _______________ hungry seven minutes ago. 8. It _______________ cold last Tuesday. 9. My friend __________________ sad nine minutes ago. 10. My parents ___________________ in the swimming pool last month. 11. I __________________ the fastest swimmer in 2011.
Add ponytails to sentences 1 - 6. Make all sentences negative. Add « tails» to 7 – 11 negativesuggestions
1. You were at the circus last Friday. 2. She was in the zoo three hours ago. 3. He was a good friend last year. 4. They were doctors in 2008. 5. Fred was happy five hours ago. 6. The days were cold and wet last September. 7. Ann was ill last Monday. 8. You were in this part of the country yesterday. 9. She was at the library yesterday. 10. He was at the seaside last summer. 11. The weather was sunny yesterday and the day before yesterday.
Answeron thethe questions
1. Were you happy last week? 2. Is Helen beautiful? 3. Your teacher is very kind, is not she? 4. Emily and Kate were students a month ago, were not they? 5. The news was not important yesterday, was it? 6. Charlie is not his best friend, is he? 7. Is Sue in the museum? 8. Were you a director of a large company last year? 9. Willy and Eve were on a business trip yesterday, were not they? 10. Sally is at home, is not she? 11. Jack is not in the garden, is he?
Translate the following sentences into English
1. We were young 20 years ago. 2. They are from the UK. 3. Lisa is their cousin, isn't she? Not. 4. Your favorite sport was golf last month, isn't it? Yes. 5. The hamster was not in the cage 6 minutes ago, right? Not. 6. His grandmother is not from Brazil, is it? Yes. 7. Today is Friday? Not. 8. Paul and John were in London yesterday? Yes. 9. I was not at school last week. 10. He is not a doctor. 11. She is a singer.
Ask a question to the subject and give a short answer to it.
1. She was married last year. 2. The show is terrific. 3. We were in Paris yesterday. 4. The roads are slippery. 5. They were late for work yesterday. 6. My shoes are too tight. 7. The entrance door is closed. 8. Bob was ashamed yesterday. 9. The trucks are too dirty. 10. Ann’s cherry pie was delicious yesterday. 11. I was busy four hours ago.
Answeron thethe questions
1. Were you the first year student in 2011? 2. The children are at home, are not they? 3. Who was in the museum yesterday? 4. Is your uncle a director of a large company? 5. The students were not in France last week, were they? 6. Who is at home? 7. Is Mary ready? 8. His parents were married in 2005, were not they? 9. Who is Italian? 10. Her mother is not from Japan, is she? 11. Who was late for work last Friday?
Translateon theenglishtongue
1. Russia is a big country, isn't it? Yes. 2. We were students 6 years ago. 3. We are a family. 4. I am not sad. 5. He was not at work last month. 6. Bob was not your friend in 1999, was he? Not. 7. Who is your cousin? Liza. 8. Who was in Thailand yesterday? Is he. 9. Are you from China? Not. 10. Was your favorite sport golf last year? Yes. 11. We were in Poland in 1993.
Correct the mistakes
1. I is lazy. 2. Are you naughty? Yes, am I. 3. He not is kind. 4. She were a pupil last year. 4. We are not businessmen a year ago. 5. Your friend was a teacher in 2016? No, I was not. 6. Your uncle were a driver last month, were not he? Yes, was he. 7. Her parents is not doctors, is they? No, are they not. 8. Who am a vet? They were. 9. Was I a shop-assistant a month ago. 10. Is you at the party? Yes, I are. 11. He am not in Kongo.
Ask all possible questions to suggestions.
1. Mary and Adam are married. 2. The show was terrific yesterday. 3. She is in Paris. 4. The roads were slippery yesterday. 5. I am busy. 6. He was at home two hours ago.
Sample: Sara and Ann were on holiday last month. Were Sara and Ann on holiday last month? Sara and Ann were on holiday last month, were not they? Sara and Ann were not on holiday last month, were they? Who was on holiday last month? Where were Sara and Ann last month? When were Sara and Ann on holiday?
Make sentences from words. Translate any 6 sentences
1. Fred, or, is, angry, kind? Is, he, angry. 2. Was, nice, she, girl, year, a, last. 3. Am, a, I, not, pupil. 4. Were, friends, where, your, yesterday? Were, Great Britain, they, in. 5. Tom, Bess, are, and, seven? No, ... 6. Was, and, last, who, brave, kind, year? They __________________. 7. Am, I, happy. 8. Were, last, we, not, friends, month. 9. Jill, Tim, nice, merry, are, and, and? Yes, _______________________. 10. A, slim, fat, is, boy, or? Is, he, fat. 11. Was, six, ago, where, Tom, minutes? Was, home, he, at.
Instruction manual
Start explanation the verb “To be” with some general words about the differences between Russian and english languages. Tell me children about that in in English language, unlike Russian, not three forms of time, but twelve. Explain that there are so many because russian the language belongs to inflective languages, that is, those in which the main meaning of the words is conveyed by their endings. In English, meaning is conveyed through special constructions and auxiliary words, and that is why verbs in English can perform different functions. For example, the verb “to be” can be semantic, auxiliary, and modal.
Tell me children about what these terms mean - semantic, auxiliary and modal, as an example the verb "To be." Explain that when this verb is semantic, it is used in its main meaning, that is, as the verb "to be, to appear, to be." Say that in russian language, this verb is omitted in the present tense, but is preserved in the past and future. For example: “I am a schoolboy. I was in children’s the garden. I will be a student. " In English, the verb “to be” is never omitted, moreover, it is the only verb that changes in faces and numbers in Present Simple, and in Past Simple it has two forms at once - for the singular and for the plural the numbers . In other times, “to be” loses its individuality and forms temporary forms in the same way as all other verbs.
Ask children remember separately, that in the interrogative and negative forms Present and Past Simple, the verb “to be”, unlike other semantic verbs, does not need helpers, that is, auxiliary the verbx so to tell "Is self-service."
Hand out children schemes reflecting various forms the verb "To be" in various forms the verb. Fix the material with exercises on the subject and have the children learn the “to be” forms.
The whole system of verb forms, depending on the ability to change according to persons, tenses, moods, breaks up into conjugated and non-conjugated forms. Non-conjugated forms include the infinitive, participle and participle. All other forms are conjugated. But more often consider conjugation as a change in verbs by numbers and persons. The choice of writing unstressed vowels in personal endings depends on the correct conjugation of verbs.
Instruction manual
Determine in what time worth the verb. Change verbs by numbers and persons only in the present tense and simple future, in the past tense do not conjugate verbs! Verbs in the complex future tense only conjugate the auxiliary verb to be, leave the main verb unchanged, i.e. in the form of an infinitive. Notice the verb BE conjugates in the future tense, and in the third person present tense used forms are and the essence.
Put the verb with an unstressed personal ending in an indefinite form, i.e. he must answer such questions: what to do? what to do ? For example: draws - draws, stands out - stands out, breathes - breathes, runs - runs.
Put the word in the following forms:
Singular
1 face (s) - I draw, highlight, breathe, run
2 face (you) - draw, highlight, breathe, run
3 face (he) - draws, highlights, breathes, runs
Plural
1 face (we) - draw, select, breathe, run
2 face (you) - draw, highlight, breathe, run
3 face (they) - draw, highlight, breathe, run.


