Friends, hello everyone!
So, below we will consider what is possible and what cannot be written in business, formal (informal) and everyday, informal (informal) letters (letters):
What can be used in informal letters.
Contractions - I mean abbreviated forms of denial, etc., for example, didn’t, can’t, I’d like to etc.
Paul doesn’t want to go to California now.
(Paul doesn't want to go to California now)
She didn’t cook cupcakes.
(She didn't make cupcakes)
Idioms (idioms) - In informal letters you can use idioms and winged expressions. For example, hit the books (study hard), sleep like a log (sleep very hard) ...
I’ll sleep over in my friend’s house about a week.
(Almost a week I will live with a friend)
Phrasal verbs (phrasal verbs) - This refers to verbs that consist of a verb (verb) and a preposition (preposition). For example, give up (to give up), shout up (to shut up), etc.
We want to order in some Mexican food.
(We want to order some Mexican food)
I’m dressing up for my prom.
(I dress up for my graduation)
Imperatives (imperative). Also, in informal letters imperative is allowed.
Don’t write me!
(Do not write to me!)
(Go to sleep!)
Really (actually), very (very), totally (absolutely) - in an informal letter you can safely use these words.
I can totally agree with your opinion.
(I can completely agree with your opinion)
We really enjoyed this vacation.
(We really enjoyed this vacation)
On top of it all / To top it all off(Besides all this / to complete it all) - similar expressions are often used in life when writing informal letters.
On top of it all John also quarreled with me.
(Besides all this, John also had a fight with me)
Abbreviations (abbreviations) - in english language there are many abbreviations for informal messages and letters. For example, Lol (laugh out loud), RIP (rest in peace) - “rest in peace”, etc.
We are hanging out tomorrow in my house. BYOB (bring your own booze / beer) if you’re coming.
(We’re hanging out at my place tomorrow. If you come, take your drink with you)
A lot (many), this is an informal, colloquial form (much) and (many).
I’ve got a lot of toys. Let’s go! We will play something!
(I have a lot of toys. Let's go! Let's play something!)
Non latin based words (no words with Latin roots), since, as a rule, these are official and scientific formulations. For example, the word intelligent (smart) is a word with Latin roots and is synonymous with more everyday words like “smart, clever” (smart).
Emma is such a smart girl! She’s only 3 years old, but already can read.
(Emma is such a smart girl! She is only three years old, but she already knows how to read)
What can be used in formal letters.
No contractions - if in informal letters you can, for example, write “can’t”, then in this case, you need to write in full, that is, “can not”.
I would like to have my tea after 10 minutes, because at that time it will be directly 5 o’clock.
(I would prefer to drink my tea after 10 minutes, because then it will be exactly 5 o'clock in the afternoon)
No idioms (no idioms) - in business letters, the use of such expressions is inappropriate.
I tossed and turned last night, so I couldn’t come to work on time.
(I returned all night and could not sleep, so I could not come to work on time)
You can’t say that! And you need this:
I could not come to work on time, because of my feeling unwell in the last night.
(I could not come to work on time, because of my poor health last night)
No Phrasal Verbs (no phrasal verbs) - it is necessary to change them with more official words.
Our group of scientists discovered (instead of "find out" (instead of "find out")) this new kind of butterfly.
(Our team of scientists discovered the new kind butterflies)
No imperatives! (No imperative!) - This is considered incorrect and is not allowed in business and strict letters.
You may send the cargo at your earliest convenience.
(It is necessary that you send the goods at your earliest convenience)
Strongly (very, strongly) - instead of the words "vary, totally, really", you must use this word.
I strongly advise to expand the range of goods.
Furthermore, moreover (in addition, besides) - Such formulations are very suitable for business style. Using them - you will not be mistaken.
We do not change our position. Moreover, we are going to develop our projects.
(We do not change our position. In addition, we will develop our projects)
No abbreviations - if these are not the names of firms or organizations, then do not use abbreviations. For example, you need to write “Television” (TV), not “TV”.
Our channel will produce new television show.
(Our channel will release a new television show)
No "a lot" (no "a lot") - you must use the words "much / many".
Many employees will participate in meetings.
(Many employees will participate in rallies)
Latin based words - as already mentioned, these are scientific and official words.
You are all intelligent gentlemen and you clearly understand what we intend to do.
(You are all smart gentlemen, and clearly understand what we intend to do)
Learn English, friends, and take care!
Exam offers an excerpt from a letter from your potential pen friend. The letter contains some news and several questions where you are asked for opinions, advice, etc.
It is required to write a response letter, starting with your short return address in the upper right corner, the date under the address, greetings and ending with a farewell phrase and name.
First of all, in order to write a letter, you need to know the rules of spelling and punctuation of the English language and try to follow it - the one to whom you addressed the letter will be pleased to read a correctly composed letter.
One of the tasks in the English language in both the exam and the exam is writing a personal letter in response to a letter from an “English-speaking pen pal”. It is included in Part C, as is the writing of an essay in English. Moreover, while in the Unified State Examination the volume of the letter is 100-140 words, in the Unified State Examination the limit is set to 100-120 words, because in the Unified State Examination the task is given to ask 3 questions, and in the Unified State Examination - simply to answer the letter, although, in any case, if you write questions, this will be a plus.
Writing a letter to foreign language is a simple task that must be completed as quickly as possible in order to leave time for other tasks. So, we will consider uniform rules for writing a personal letter. To make it easier to understand everything, see the specially selected video site:
In the upper right corner indicate the address in the following order (reverse order to Russian):
- apartment
- house number, street name
- town
- the country
It is allowed to indicate the address in a short form, for example:
Moscow
Russia
Under the address skipping a line, you must write the date of the letter:
June 4th, 2012
June 4, 2012
or less formally:
04/06/12
The letter begins with an informal appeal. If the name of your interlocutor is not indicated in the task, you should think of it:
Dear Tim,
Dear Rebecca,
After treatment, you need to put a comma!
Divide the text of the letter into several logical paragraphs, each of which begins with a red line.
1. In the first paragraph, you should thank your friend for his letter:
Thanks (a lot) for your (last) letter.
Your last letter was a real surprise.
I was glad to get your letter.
It was great to hear from you! / It was great to hear that ... / I was happy to hear ...
You can also apologize for not writing before:
Sorry I haven’t been in touch for so long.
I’m sorry I haven’t answered earlier but I was really busy with my school.
and / or mention any fact from the letter received:
I’m glad you passed your History test!
Sounds like you had a great time in London!
Great news about your ...!
2. The main part of the letter (2-3 paragraphs). In it you must disclose all aspects specified in the assignment. Do not forget to ask the necessary questions.
It is assumed that the letter should be written in an informal style, so you can use informal bundle words such as well, by the way, anyway, socolloquial expressions like Guess what? Or Wish me luck !, as well as exclamation points.
3. In the last paragraph, explain why you end the letter:
Well, I’d better go now as I have to do my homework.
Anyway, I have to go now because my Mum asked me to help her with the washing up.
I’ve got to go now! It’s time for my favorite TV show.
and mention further contacts:
Write (back) soon!
Take care and keep in touch!
Drop me a letter when you can.
Hope to hear from you soon.
I can’t wait to hear from you!
At the end of the letter, on the separate line, the final cliche phrase is indicated, which depends on how close the author and the addressee are. A comma is always placed after it! The following are possible options from the least formal (1) to the more formal (8):
- Love
- Lots of love,
- All my love,
- All the best,
- Best wishes,
- With best wishes,
- Yours
- Warm regards,
On the next line, under the final phrase, the author’s name (without a surname!) Is indicated. For instance:
Andy or Kate
Thus, a letter to a friend has the following form:
The address of the writer (indicated in the upper right corner)
Date of letter (under address)
Appeal,
At the beginning of the letter, the author usually a) thanks the addressee for previously received correspondence; b) apologizes for not writing before.
The main part of the letter (2-3 paragraphs). It must be disclosed
all aspects specified in the assignment.
Do not forget to ask all the necessary questions.
At the end of the letter, the author usually mentions the reason for the end of the letter, as well as further contacts (cliché phrases are used).
The final phrase
Signature of the author (name)
Template for writing a letter in English
13 Ostozhenka street
I was so happy to get your letter! I can’t wait to meet you in July! I’m sorry I haven’t answered earlier but I was really busy with my school.
You asked me to tell you about ... Well, ...
By the way, ...? ...? ...?
Unfortunately, I’d better go now as I’ve got loads of homework to do (as always). Take care and keep in touch!
Personal Email Example
You have received a letter from your English- speaking pen-friend who writes
... All in all, my birthday party was great! However, one of my friends came to the party in casual clothes. Just jeans and a T-shirt! Of course I didn’t say anything but she felt a bit left out. I was really sorry for her! And what do you usually wear when you go to a birthday party? Is it important in Russia to wear smart clothes at parties? What would you do if you were me?
If you have to write a letter in English, the first thing you should think about: the style or register of writing your letter (register). How to determine the case? Think of three aspects:
The less you know the recipient, the more formal your style should be. There are such styles of writing letters in English: formal (formal) and informal (informal). Semi-formal or neutral (semi-formal or neutral) style is also distinguished, but by its nature it is closer to formal. Some authors distinguish the following styles depending on the type of communication, addressee and language means:
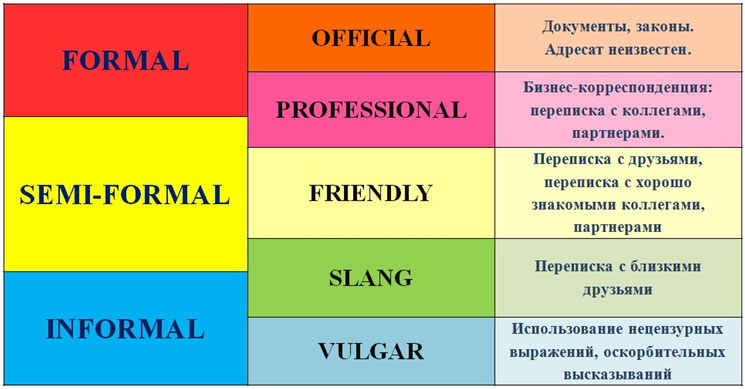
The formal style is inherent in documents (for example, legal), high-level business letters, in a formal style all the rules of punctuation and grammar are respected. Semi-formal style is used for business correspondence, professional communication. Since the author and recipient of the letter are usually busy business people, letters of this style are specific, focused on facts and include a standard, template language. And, finally, the informal style is typical for correspondence of friends, communication in social networks. It involves the use of colloquial expressions, abbreviations, grammar rules and punctuation are not always respected.
However, these are just general differences between styles. In this article, we will consider more fundamental distinguishing features that will help you write high-quality letters in English.
1. Vocabulary
If you compare two identical in content, but written in different writing styles, then an informal letter will be shorter. Do you know why? Because the formal style involves the use of longer words, words of Latin origin. Unlike the informal style, phrasal verbs are practically not used in the official style, except for those that cannot be replaced with a longer equivalent. The same applies to nouns: if when writing an official letter you have a choice between a short word and a long one, choose what is longer.
Let's look at some of the differences between formal and informal vocabulary:
|
Verbs (Verbs) |
||
|
Informal |
Translation |
|
|
to ask, to request |
||
|
be the cause of |
||
|
check |
||
|
deal with anything |
||
|
find out |
||
|
repair |
||
|
receive |
||
|
get in touch with |
to contact |
|
|
give, provide |
||
|
decrease |
||
|
increase |
||
|
leave out |
||
|
allow |
||
|
need |
||
|
apologize |
||
|
seem |
||
|
set |
||
|
show |
||
|
inform |
||
|
Nouns |
||
|
Informal |
Translation |
|
|
chief |
||
|
opportunity |
||
|
facilities |
||
|
aged people |
||
2. Use of passive voice
In an informal writing style, the use of active voice prevails over use. Informal letters are more personalized, while formal letters and documents speak of facts. Consider this with examples:
I invite you to come to my party Friday evening. “I invite you to come to my party on Friday night.”
You are invited to attend annual conference. - You are invited to attend the annual conference.
The teacher told us to complete the test papers. - Teacher told us to finish the test assignments.
The students were told to complete the test papers. - The students were told to complete the test assignments.
The camera you delivered to me yesterday is broken. “The camera you delivered me yesterday is broken.”
The camera which was delivered to me yesterday is flawed. - The camera that was delivered yesterday is defective.
In each pair of sentences, the first refers to the informal register. As you can see, every second sentence, presented in the official style, tells the facts and sounds more neutral and formal.
3. Conversions and stereotypes
A characteristic feature of the informal style is first-person appeals, using I: I am sorry ..., I think ...etc. While official letters are based on cliches, standard phrases of business communication. The informal style makes it possible to improvise, and the formal style is more stereotyped.
I am sorry for my being late. “I apologize for being late.”
We apologize for the delay. “We apologize for the delay.”
I am glad to tell you that I am coming soon. “I am pleased to inform you that I am coming soon.”
We take pleasure in informing you about our forthcoming visit. - We are pleased to inform you of our upcoming visit.
Typical of an official style is the use of the pronoun we. When a representative of one company writes a letter to another company, the letter is written not from the first person singular (I), but from the first person plural (we).
4. Slang expressions
Slang expressions are absent in the official style, they simply are not there. The same goes for most idiomatic expressions. Formal style is the language of specificity and business vocabulary, therefore, the use of slang is unacceptable, it is a sign of unprofessionalism and disrespect for the recipient:
He wrote us about stuff. “He wrote to us about all kinds of nonsense.”
He sent us information on the question. “He sent us information on this.”
5. Abbreviations
The informal style, along with slang expressions, allows the use of abbreviated forms of the verbs to be, have, has, would, will and others: I "m, we" ve, he "s etc. They are never used in the official style, all forms must be written in full: I am, we have, he is, they will, she would etc.
6. Concrete appeals and impersonal constructions
In informal letters, to a friend, for example, we refer to a specific person, calling him by name in his letter. Official letters are impersonal, they are not addressed to anyone, the name of the addressee is not used in the main part of the letter, only at the beginning. Imperative constructions in official letters and documents are replaced by passive ones, that is, you do not give instructions, but formulate the rule:
If you have questions, feel free to ask me. - If you have questions - do not hesitate to contact me.
You will be contacted for further information. - You will be contacted for further information.
7. Harmonization of ideas
Even unions of formal and informal style have their own differences. In informal communication, we use the familiar set of phrases and expressions to combine our ideas. Most of them are short: and, but, also, because. Unions that are used in the formal register are usually long words or phrases. Consider the table and compare some of them:
|
Informal |
Translation |
|
|
due to (the fact that) |
as a result because of |
|
|
in addition |
||
|
thus |
||
|
otherwise |
||
|
provided that |
||
|
moreover |
The word also as a union should be avoided in a formal style, but it is quite acceptable to use it if it refers to a verb (in constructions or inverted sentences):
Also see the agenda attached. - Also check out the attached action plan.
Also covered accommodation expenses. - Also reimbursed living expenses.
As you can see, formal and informal styles in English are fundamentally different from each other. The main distinguishing features are:
- vocabulary
- grammar, the use of active and passive voice
- the use of phrasal verbs, slang expressions
- use of speech patterns, cliches
- shortened forms
- alignment of ideas
Thus, when you start writing a letter in English, remember about the differences in the registers, watch out for vocabulary, grammar, and other language means so that your letter is designed in the same style.
If you liked this material, share your feedback and subscribe to our updates.


