Objectives: the formation and activation of the use of vocabulary in speech.
Tasks:
1. To familiarize with new vocabulary on the subject of "Meals", to train in listening and eating.
2. To develop the ability to understand coherent statements by ear, to respond to different kinds questions.
3. Control of phonetic skills.
Teaching aids:
-Pictures with images of food and layouts on the topic;
- animal toys;
Doll John Cook;
-cassette with phonetic exercises;
The course of the lesson.
1. Organizational moment-Warming up activity.
Teacher: Good morning, children! Children: Good morning, G.V.
Glad to see you! Glad to see you!
How are you? I’m OK, thanks! And how are you?
I’m fine, thank you
2. Phonetic charging.
And how is our friend Tongue-? Mr. Tongue?
How does he “rejoice”? -
How is “upset”? -
Like Mr. Tongue knocking out dust? , poem “Tick-Tock” Tick-tock! Tick-Tock!
Says the clock, says the clock!
(Training of other sounds using rhymes, pay special attention to the sound [r] and combinations with this sound - bread, - green; long-short vowel -soup, -meat)
3. Introduction to the plot of the lesson. Listening to familiar structures.
- Guys, today we are going to visit my friend John, his name is John Cook.
And who will come with me? How many of us? Let's count (Let’s count!) Children: 1, 2, 3, ...
- How many girls? (How many girls?) Children: 1, 2, 3 ...
- How many boys? (How many boys?) Children: 1, 2, 3 ...
(The teacher addresses the children T -Ch, T-P1, P2 ...)
What is your name?
Where are you from?
Have you got a mother?
Have you got a dog?
Can you jump?
What can you do?
4. Physical education.
Execution of commands.
T-Ch, T-P1, P1-Ch, P1-P2 (Teacher-Children, Teacher-Scientist, Scientist- Children, Scientist-Scientist)
We use verbs (go, run, jump, swim, sleep, fly, dance, clap, sing, eat, drink, etc.)
Let’s go to my friend John!
5. Familiarization with the new vocabulary on the subject of "Food".
This is my friend John Cook. He is a cook. ("Cook" is a language guess in appearance)
J.C .: Hello, children!
Children: Hello, John Cook!
(John Cook sings a song) Ding-dong-dell! Ding-dong-dell! Soup, meat and potatoes ...
J. Cook sings a song and calls us for lunch. And what has he prepared for us? What do you think?
Soup- (language guess) - show the picture –repeat 3 times.
Meat- (language guess) - show the picture –repeat 3 times.
Potato- (remember the counter “One potato, two potatoes, ...”) show the picture - repeat 3 times
And what did he cook for the mouse? Cheese- repeat picture 3 times
And for the bird? (a bird) Bread - repeat picture 3 times
For a cat? (a cat) Butter - repeat picture 3 times
For a dog? (a dog) Sausages-picture-repeat 3 times
6. Practice vocabulary.
And where are our animals? Where are they? Oh where? Oh where?
Let's all together call their favorite treat, they will hear and come running!
(We work in the mode T-Ch-P1, P2 ....)
We show the picture (cheese) - T- “cheese” -Ch - “cheese” (3 times) - P1- “cheese”
A little mouse runs up: “I’m here. I like cheese ”
(bread, butter, sausages, soup, meat, potato). All the animals gathered.
7. Training in use new vocabulary.
The game "What is missing?"
Guess the game! (What does the mouse like? What do you like? What do I like?)
We have to go back to kindergarten. Let's say goodbye to John and ask him to cook us something “tasty - sweet” another time.
Children: Good- bye, John Cook! John Cook: Good -bye, children! See you soon!
Title: Summary of the English language lesson in the preparatory group of the kindergarten “Food. Visiting John
Position: teacher of additional education
Place of work: MOBU NOSH-DS №80, Sochi
Location: Sochi, Krasnodar Territory
Training program
English, preschool (4–5 years)
Teaching English to preschoolers has its own characteristics, which are based on the psychophysiological development of children of this age. Psychologists say that the perception, memory and attention of preschoolers are involuntary. Children do not know how to control their perception, cannot independently analyze this or that subject. For children's memory, exceptional photographic features are characteristic, but at the same time, the preschooler does not care that everything that he perceives can be recalled later. A characteristic feature of the child’s attention is that it is caused by externally attractive objects. Focused attention remains until interest in perceived objects remains. Many fundamental speech skills and abilities are not yet available to preschool children, which is associated with a greater development of the right hemisphere of the brain compared to the left. This leads to the fact that children of preschool age cannot build complicated logical chains, replace words in similar phrases, perceive a phrase as a set of lexical units, etc. Therefore, training should be based on these features and significantly different from primary school .
IN kindergarten “Baby” learning English begins in groups of children of 3 years of age, and ends in groups of children of 5-6 years of age. We distinguish 3 stages:
Stage I - 3-4 years,
Stage II - 4–5 years
Stage III - 5-6 years.
At each stage, the program is built taking into account the characteristics of children of this age.
The main teaching technologies for preschoolers are based on a harmonious combination of 3 teaching methods:
1. gaming
2. communicative,
3. techniques for the full inclusion of the whole organism (total physical involvement).
Throughout the entire training, the unity of the forms and types of work is maintained, while the visualization and imagery dominate, as the phrase is perceived by the child not as a set of separate lexical units, but as a block, something single, whole, image.
This program is designed to educate children 4–5 years old and takes into account the peculiarities of their psychological and physical development. The age of 4 to 5 years is called the age of “why.” Children over 4 years old are able to mentally imagine what they have never seen. They love to listen to adult stories and ask a lot of questions. Thinking makes a quantum leap: the child goes beyond the limits of static being and begins to live in a world extended in time. This allows you to move on to the search for patterns that underlie the world’s structure. He becomes interested in processes as ordered systems of events. In this regard, it is necessary to include elements of the laws of the linguistic system in training. At the same time 1) not to depart one iota from the basic principle of visibility and imagery; 2) be guided by the principle of “do as I do”, “speak as I do”; 3) to learn a language exclusively in practice, without even applying elementary theoretical linguistic concepts (teacher centered method).
Targets and goals
The main purpose of the course is to familiarize children with simple vocabulary that is accessible and relevant to them level of development, the introduction of elementary linguistic constructions, the upbringing and development of personality through the introduction to the culture of English-speaking countries using children's folklore. These goals determine the main objectives of the course:
1. Familiarization with the basic sounds of the phonetic structure of the language and the further development of the child’s speech apparatus.
2. The formation of the ability to understand the simple commands of the teacher and respond to a number of elementary questions.
3. The development of elementary language skills and abilities (the ability to respond to teacher commands, answer simple questions, learn accessible vocabulary).
4. Development of language memory (photographic, figurative, graphic, verbal) and creative abilities.
5. The formation of skills to understand elementary linguistic phenomena and the ability to compare simple holistic constructions as a block on native language in comparison with the studied.
6. Broadening the horizons of children and their general culture.
7. Development of skills in a large group (12-14 people) and in small groups of 5-6 people, the ability to work in a team.
Types and forms of work
Fundamental aspects of the concept of preschool education are reduced to the use of a wide range of methods, techniques, forms and means of instruction. This takes into account the individual characteristics of children, as well as the features of their general cultural development and microsocium - the family. So, the main techniques:
a) imitation;
b) the creation of images: visual, musical, plastic. As a result - the dominance of non-verbal learning tools in the classroom (pictures, images, music, dances);
c) the use of educational games;
d) riddles;
d) the dramatization of mini-performances, which helps to eliminate the psychological barrier in children, increase self-esteem, significance, which implies a success technique.
Work principles
1. It is imperative to use various means of encouragement, both verbal and material.
2. Form at children a positive image of the teacher, which increases the reflective abilities of the child.
3. To limit the teacher’s speech in Russian to 5–10%. (The child's speech in English is 90%).
4. Systematically introduce vocabulary:
The first lesson is 3 words.
The second lesson is consolidation.
Subsequent classes - activation using speech structures + 3-4 new words.
5. Take into account the short-term memory of children at this stage of development, systematically return to previously passed material and include it in subsequent classes.
6. To teach full speech structures, which contributes to the development of speaking skills.
7. Give preference to pair and group training. This helps to establish a favorable psychological climate in the group and removes language barriers.
8. Develop responsiveness to teams and teacher questions.

The teacher in the classroom uses the following types of work:
1. Work on pronunciation.
a) fairy tale “Living tongue”
b) tongue twisters
c) rhyming
2. Work with a toy.
a) dialogue with the toy
b) description of the toy
3. Work with a picture.
a) picture description
b) the game “What has disappeared”
c) “Find a picture”
4. Learning and reciting verses.
a) poetry contest
b) multi-genre recitation (optimistic, sad, angry, etc.)
5. Learning songs.
“Show” a song
6. Staging short stories and plays.
7. Outdoor games.
8. Calm games.
9. Creative games.
10. Reproduction of situational dialogs.
11. The story in the picture.
12. Learning letters.
Organization of work in a group
In the classroom, children sit and stand in a semicircle or circle, as close as possible to the teacher, which helps them to see and hear the teacher well and creates a warm psychological climate, and also allows you to quickly change activities. The lesson is built on a systematic scheme, which from time to time should vary slightly as you progress through the training stages.
Sample lesson plan
1. Greetings.
2. Phonetic charging.
3. Repetition of the lexical material.
4. Warm up using outdoor games.
5. Activation of the past and the introduction of new lexical material.
6. Learning poems and rhymes.
7. View English cartoons.
Course structure and content
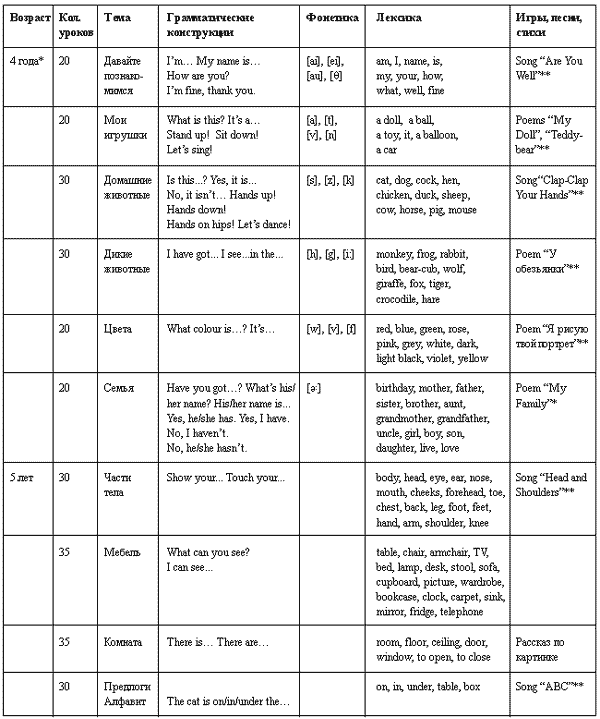
When choosing topics, lexical and grammatical constructions, the level of development of children, their motivation and interests, as well as their correlation with curricula for the development of cognitive abilities and speech in Russian in a kindergarten are taken into account. At the stage of teaching children 4–5 years of age, based on the experience of teaching English to children of this age, it seems appropriate to introduce the following 11 topics:
The increase in vocabulary and the expansion of grammatical structures in the second stage occurs by gradually introducing new lexical units and complicating grammatical constructions (an increase of about 40% compared with the stage of teaching children 3 years old). By the end of the education at the II stage, children have acquired approximately 150-180 lexical units.
Classes with preschool children should be carried out at least three times a week for a duration of 20 to 25 minutes. It is most effective to organize these classes in the morning (from 10 to 12 hours).

Methodical literature, educational complex and visual material used in English classes in kindergarten.
1. The development of intellectual abilities of a student, Tikhomirova L.F. Yaroslavl, 1996.
2. Math for kids, Serbina E.V., M .: Education, 1992.
3. What doesn’t happen in the world, ed. Dyachenko O.M., Agaeva E.L., M .: Education, 1991.
4. The development of logical thinking of children, Tikhomiro-va L.F., Basov A.V. Yaroslavl, Tringo, 1995.
5. Development of cognitive abilities of children, Tikhomirova L.F., Yekaterinburg, 2003.
6. CMD How can we learn kids to speak English?, Dolnikova R.A., Fribus L.G., St. Petersburg, KARO, 2002.
7. Teaching foreign languages \u200b\u200bin kindergartens, Chistyakova T.A.
8. Foreign languages \u200b\u200bat school, 1990–2004, NMZh Moscow.
9. UMK English-1 Vereshchagina I.N. M. Enlightenment, 2001.
10. Disney's Great Dictionary, Walt Disney Production, 1996.
11. Round and round the garden, Peter Gross, 1978.
12. Handwriting, Zaner-Bloser, Inc., Columbus, 1987.
13. Sing out Zdorova B., Moscow, Education, 1990.
14. Enjoy English, N.Rowell, Title, Obninsk, 1997.
15. Welcome, E. Gray, V. Evans, Express Publishing, 2001 (with cards and video course).
16. Letterfun,E. Gray, V. Evans, Express Publishing, 2001 (with video course).
17. UMK Bravo
18. Muzzy in gondoland, BBC English, “Infa-M”, 1990.
19. English for kids - 1, 2, Workshop of Igor Shadkhan, 2000.
20. English for kids, Home Video, 2000.
21. Set Sail - l, 2, E. Gray, V. Evans, Express Publishing, 2001.
22. Theme nights in English, Diment A.L., M. Enlightenment, 1988.
23. CMD Happy english, Indian Art Press, New Delhi, 1990.
24. Easy Picture Words 1-2, cards.
25. King size, KoHTyp-M, St. Petersburg, 1992.
26. “Happy English” lotto.
27. A training set of numbers, letters and signs with magnetic fastening.
M.A. Bolkhovskaya
D / Garden "Baby", St. Petersburg
* In groups of 4 year old children, classes last 20 minutes, 5 year olds - 25 minutes.
** Dolnikova R.A., Fribus L.G.As kids we learn to speak English. SPb .: KARO, 2002.
Control is carried out after passing through each topic. For this, one lesson is allocated for repetition and consolidation, as well as for the identification of words and constructions that need additional training.
English lesson in kindergarten
English teacher
Kindergarten "Aygolek"
Karasai district, Kaskelen
Chikina Tatyana Konstantinovna
Lesson topic: « Toys»
Lesson Objectives:
Developing:
- teach children the ability to listen to the teacher;
- develop the ability to answer the question How many? Name the letter D, the correct pronunciation;
- develop and maintain interest in learning foreign language.
Educational:
- creating conditions for communication in the process of the lesson;
- To foster interest in the account, interest in the English language in general;
- teach children the ability to respect each other.
Practical:
- activation of the studied structures in brief statements on the topic;
- teach to use interrogative expression How many? And the expression I have got;
- teach to use the plural of nouns;
Lesson features:
Audio recordings of songs. Toys are a robot, a typewriter, a doll, a ball, cards with numbers from 1 to 10, a magnetic board, the video “Number song counting from 1 to 10” for repeating the score.
Equipment: laptop.
During the classes:
Greeting.
Teacher: Good morning, children!
Children: Good morning, good morning! Good morning to you!
Good morning, good morning! We are glad to see you!
Teacher: I am glad to see you. Let’s begin our English lesson. How are you?
Phonetic charging. LetterC, Sound [k]
Johnny: Hello kids! I’m happy to see you again. Let’s have fun together. Repeat after me: [k], [k], [k], [k] cat-cat-cat.
I like [k]. I like [k]. Cat, cat, cat starts with [k]. Camel, camel, camel starts with [k].
Teacher: Today we’ll learn how to count to ten. Say after me: one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten. (watching a cartoon about numbers from 1 to 10).
Teacher: Now, let's watch the video again and repeat the score from 1 to 10 for the chicken. Are you ready?
Children: Yes, we are.
Teacher: Let’s count then. One, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten!
Children repeat the words for the teacher.
Foxy appears (toy fox).
Foxy: Good morning, kids!
Teacher: Good morning, Foxy. How are you?
Foxy: I’m fine. And how are you teacher?
Teacher: I’m OK!
Foxy: Hello, kids, how are you?
Children: Hello Foxy!
Foxy greets every child, asks the question, “How are you?”
Teacher: The guys, and the fox Foxy, met our friends: Batyr, Dana, Dima and Ira. But they didn’t come empty-handed, they want to show us their toys - toys.
Teacher: Let's invite them in. Come in!
Let's say please in English. How in English "please"? Right, please!
Children: Please come in!
Teacher: Let's see what kind of toys the guys have and call them in English: a machine - a car, a ball - a ball, a robot - a robot, a doll-doll.
And let's sing a song to remember new words:
One and two, (girl singing)
A robot for you.
One and two, (boy sings)
Teacher: Oh, here you are. Have you got a toy?
Foxy: Yes, I have. I have got a car. (Showing his toy.) Have you got a toy?
Teacher: Yes, I have. I have got a cat. I have got means "I have," "I have." Let's say in a whisper, “I have got.” Now shout “I have got!” Loudly Now let's play the game “Echo”. I have got a (ball, doll, car, robot).
Teacher: Well done, good for you- let's clap your hands. Clap your hands.
Physical education "Clap your hands." (Video children repeat movements)
And look at the picture of whom you see? That's right for a boy and a girl, and how a boy will be in English is a boy, - good for you, and a girl - a girl- good for you!
And let's see you are a lot in the group, so we add the ending to our words – sSo we got the plural - boys-, -girls-. And now let's play the game, I say boys - boys raise their hands, I say girls- girls raise their hands. Young guys! Let's repeat a boy- boys, a girl- girls.
The teacher takes out a soft toy of a teddy bear from a bag -bear.
Teacher: It’s a toy. And now let the guys name the toys that we already know. And if you forget what they are called in English, Foxy will tell you.
Children call toys: It’s a doll. It’s a ball. It’s a car. It’s a robot.
The teacher takes out toys from the bag, using their names with a definite article - a -
Teacher: Very well! And our heroes want to know if we know the score in English. Now they will ask us questions in the picture, and we will answer. How many boys? How many girls? How many robots? How many dolls? How many cars? How many balls? (children answer questions)
Teacher: Let us repeat all the letters that we learned A [a] - apple
Hello kids. I’m happy to see you again. Let’s have fun together. Repeat after me: [d], [d], [d]
[d] -dragon
[d] - dad.
Explain how to pronounce this sound correctly: place the tip of the tongue on the tubercle located behind the upper teeth and pronounce the sound [ d]. Now, let's repeat for Johnny:
[d], [d], [d]
[d] -dragon
[ d] – dad. Let's colorize our letters.
Teacher:And our fox offers to play a game Didactic game "Find the word." (children look for words that start with the letter D
Teacher: Now, guys, take a simple pencil in your pen and our task will help the ball get to the toy shelf. (to develop fine motor skills of hands - circle along the line.)
Teacher: Our friends gave us toys, we need to arrange the toys
on the shelves. You have stickers in your workbooks, let's stick them and name the toys in English.
Teacher: Look, boys and girls! We met Lysenok and our guests today with toys. Let's repeat their names again. (children repeat the name of the toys) “Thank you!” Thank you! Let's thank the fox and our friends and say goodbye!
MBDOU kindergarten "Kid"
English lesson summary
in kindergarten
Prepared by: teacher
add. education Melnikova N.R.
udomlya
2012
Objectives:
Acquaintance with some features of the English language in comparison with Russian;
Refinement, expansion and revitalization of the dictionary on the topic of "animals";
Consolidation of verbal constructions in speech
(What "s your name? I am ...
How old are you? I am ...);
Introduction and refinement of new vocabulary on the topic of "numbers" (1-10);
The development of memory, attention, phonetic and musical hearing, fine, articulatory and general motor skills;
Formation of a positive attitude in the lesson, friendly relations.
Equipment:
Toys (a bear - bear, a hare - hare, a dog - dog, a frog - frog, an elephant - elephant, a mouse - mouse, a cat - cat, a fish - fish), Dunno (do-not-know ) with unfulfilled homework, recording songs ("Good evening", "1-7", "How many elephants?", "One and two and three ..")
Working process
1. Organizational moment (Formation of a positive attitude of children to participate in the lesson. Development of auditory attention.)
The game "Magic Gate". Children go through a hoop (magic gate) to get into the country of the language they are studying, greet them and give them a password (Hello. I am Sveta) and sit down.
Teacher: Do you guys like to play? (the game "Repeaters"). Then prepare your ears and repeat after me:,,,,,,.
2. The development of verbal constructions.
Show me your teacher - teacher. He nods his head and says something: "Good evening." –Song "Good evening".
In our magical land, we play, dance, talk, and our toys help us in this.
So today I brought a red bag in which all our animals are lying. Let's remember. (Children are called previously studied animals).
A bear, a hare, a dog, frog, an elephant, a mouse, a cat, a fish.
How many toys are there? 1? 2? 3? - Many!
Let's count our animals, but first we need to remember the names of the numbers. In English, I start to count with the thumb and fingers unbend. Count 1,2,3-10.Song "1-7".
3. Charging. (Development of general motility, coordination of speech with movement.)
Hands up
Hands down
Sit down
Stand up.
1, 2, 3 hop, hop, hop
1, 2, 3 stop, stop, stop.
1 and 2 and 4 and 4
I am sitting on the floor.
I am sitting on the floor.
1 and 2 and 3 and 4.
Song "How many eleph ants?"
4.Guest. (Activation of children's speech, consolidation of verbal constructions.)
Guys, an unusual guest came to us today. Call him: "Come in". (Dunno appears)
Dunno: "Hello. What" s your name? I am Do-not-know. "
Why do you think his name is that? (children's answers)
Do-not-know big or small big or little?
How old are you? I am 7.
Do-not-know came to you for help. He goes to school and he, like any other student, is given homework. But today, homework is so difficult that he cannot handle it. Will it help our guest? (Yes!)
Tasks:
- Count 1-10. Tower of cams.
- Examples: 1 + 1 \u003d
2+2=
1+2=
- Poems: to finish.
It’s not ordered to approach me to the elephant ... (elephant)
He is terribly mischievous, douses everyone with water.
Green minx, forest hopper
It’s all over the bumps, leap and lope, very playful ... (a frog).
A cat lives in a pond
Fish - on land,
I’ll say something else
Don’t listen to me.
5. The end of the lesson.
So we did our homework. Yes, and Do-not-know is time.
Good bye, Do-not-know.
And we are going to say goodbye to the magic gate and guests. Good bye


