Dyslalia is a violation of the correct reproduction of certain sounds, provided that the patient retains normal hearing function and supply of the speech apparatus with nerves. Often diagnosed in children aged 3–5 years, less often in patients of the younger school age group.
The peculiarity of the violation of the pronunciation of sounds is that dyslalia has no connection with injuries of the hearing aid or disorders of the child's central nervous system, that is, the patient is physically healthy, but when communicating, he changes letters in places or pronounces them "swallowing". However, if the child is asked to write a word with difficulty, the correct letters will be indicated.
Speech dyslalia in children of a younger age group is the most diagnosed defect. If we consider the statistics, then in medical practice such a violation was found in 1 out of 3 children aged 3-5 years, upon reaching 6-8 years, speech is corrected, and symptoms of the violation will be noticed in 1 out of 5 children. In the future, the diagnosis is made only 1% of patients.
Dyslalia has a selective character, that is, the child perfectly pronounces 90% of words, letters and sounds. If the correction is implemented in a timely manner, then the patient completely gets rid of the violation of sound pronunciation.
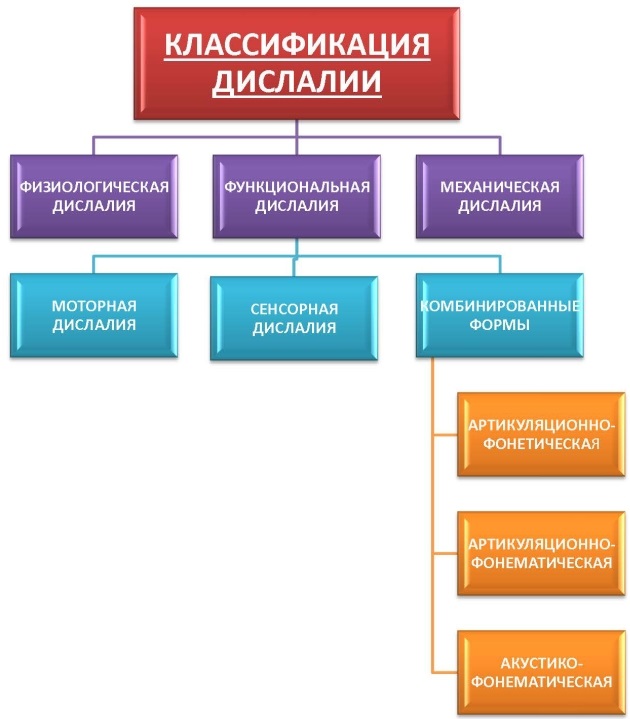
Speech dyslalia: classification of the disorder
In the process of studying the deviation, specialists came to the need to classify the pathology, which in the future made it possible to choose the optimal method of speech correction.
There are three forms of dyslalia:
- physiological - age-related speech defect of the child;
- mechanical - due to the incorrect structure of the speech apparatus (there is a possibility of hereditary transmission);
- functional - speech impairment is not caused by pathologies of the organs that are responsible for the function of speech.
With the first two forms, everything is clear. But what to do when functional dyslalia is diagnosed? Speech therapy in this case offers powerful correction methods that can help the patient. However, it is important to understand what causes it and how it manifests itself.
The occurrence of functional dyslalia is associated with stable individual characteristics of the nervous system. Violation of this type is reversible, in contrast to mechanical dyslalia, which is due to the incorrect structure of the speech apparatus, when correction is possible exclusively by surgery.
In turn, experts distinguish two types of functional dyslalia:
- sensory view - occurs against the background of neurodynamic disorders of the central part of the speech and auditory apparatus;
- motor variant - occurs against the background of neurodynamic disorders of the central part of the speech and motor apparatus.
Sensory dyslalia is characterized by a violation of the difference between similar sounds. When pronouncing, the child confuses hissing or whistling sounds, deaf or voiced, hard or soft. Therefore, when he is asked to say, for example, “word”, he can say “shlo”, that is, there is an interchange of sounds. In addition to oral speech, if the patient writes from dictation, he may make a similar mistake in writing.
Motor dyslalia is characterized by a discrepancy between movements of the lips and tongue when pronouncing sounds. Articulation becomes blurred, in connection with this, a phonetic defect appears.
In severe cases, it is possible to diagnose a set of sound pronunciation, then the doctor diagnoses sensorimotor dyslalia. The degree of difficulty in pronunciation and differentiation of sounds by the patient may be different.
By the nature of the violation, dyslalia happens:
- articulatory;
- acoustic;
- articulatory-phonetic - occurs as a result of incompletely formed phonetic hearing, when pronouncing a word, the patient incorrectly identifies difficult sounds (“crust” - “slide”, “bones” - “guests”);
- articulatory-phonemic - characterized by the replacement of the heard sound with a similar one, provided that the articulatory positions are located incorrectly (“left” - “sat down”);
- acoustic-phonemic - incorrect articulatory arrangement during pronunciation, in connection with this, the sounds being pronounced are distorted (the letter “p” is pronounced by grasing).
Depending on how many sounds the patient does not pronounce, the form of the violation is determined.
There are two forms of dyslalia:
- complex - impaired perception and reproduction of more than four sounds;
- simple - characterized by the same type of violation: monomorphic (only vowels or consonants) and polymorphic (vowels and consonants).
In speech therapy, there is a special table of violations for classifying dyslalia by sounds. The Greek alphabet was taken as the basis:
- jotacism - incorrect pronunciation of words, where there is a sound "Y";
- rotacism - incorrect pronunciation or replacement of the sound "R";
- hitism - problems with recognizing and pronouncing the sounds "X" and "K";
- cappacism - difficulties with the pronunciation of words where there is a "K";
- gammatism - incorrect differentiation of the sound "G";
- sigmatism - violation of pronunciation or replacement of hissing and whistling;
The danger of dyslalia lies in the fact that complex cumulative defects in pronunciation and sound recognition can occur against its background. In the event that a patient is diagnosed with a combined dyslalia with a phonemic deviation, the diagnosis will include a “para”, for example, parayotacism.
Causes of dyslalia
If we consider mechanical dyslalia, experts note the main reason for its appearance - a defect in physical development that does not allow the patient to correctly reproduce the sound he heard. Appears mainly in the presence of dental defects (such as abnormal bite, unerupted or malformed incisors, underdevelopment of the lower jaw, cleft palate, etc.).
Functional dyslalia develops against the background of an unstable mental or physical state of the child. This may be due to injuries.
Very often, dyslalia is diagnosed in children with mental development problems. Another factor that provokes dyslalia are diseases of high severity, transferred at the time of the formation of speech function. Often the parents themselves become the cause of the development of dyslalia, namely the lack of communication and attention paid to a preschool child who is in the active stage of speech formation.
Rarely, but there are cases of combined dyslalia.
Doctors identify a number of main causes for the development of mechanical dyslalia. These include:
- underdevelopment of the frenulum of the tongue (short);
- irregular maxillofacial bone structure;
- palate defects;
- underdevelopment of the frenulum of the upper lip;
- violation of the integrity of the upper hard palate and lips.
Given the above reasons, a speech therapist can diagnose a speech disorder, but the treatment process is transferred to dentists and orthodontists, after which the child is recommended to undergo a course of speech correction. The best results of treatment are achieved at the age of 5-6 years.
The causes of functional dyslalia are as follows:
- insufficient attention of parents to the development of the child's speech;
- the presence of an object for copying incorrect speech by a child;
- lack of upbringing of the child by parents;
- problems of phonemic hearing;
- hearing impairment.
Symptoms of hearing loss
It is not difficult for attentive parents to notice a violation of the perception or reproduction of sounds in a child. This is manifested in the distortion, replacement or omission of letters or sounds.
When a child's dyslalia is characterized by the omission of certain letters, the main symptom is their absence in any part of the word.
If sound substitution occurs, then the symptom is a change in the audible sound to a reproducible one. Such a violation occurs due to the fact that the child does not differentiate phonemes according to articulatory and acoustic aspects. With such a deviation, the patient replaces sounds in an arbitrary order, regardless of how they were formed in the original word, without classifying them into hard, soft, voiced and hissing.
When mixing sounds, the child from time to time pronounces the sound correctly or incorrectly, which indicates the incompleteness of the process of assimilation of phonemes.
If a child suffers from dyslalia, characterized by a distortion of sounds, then this can be noticed when communicating with him. Such patients use in their speech sounds or letters that are not originally present in the original word. Most often, such a defect occurs in patients with mechanical dyslalia.
If a child has functional dyslalia, then in his oral speech one can notice a violation of the reproduction of one, maximum of a pair of sounds. With a mechanical violation, the patient finds it difficult to determine a group of sounds similar to each other. In case of underdevelopment of the lower jaw, the patient will pronounce sounds by anterior lingual articulation, which is due to the inability to hold the tongue in the area of the frontal teeth.
Dyslalia refers to speech disorders that are prone to recovery. It has to do with the growth of the child. If during this period parents pay attention to the fact that their child is suffering from a disorder and seek qualified help, then the chances of recovery are high. However, even those children who did not undergo speech correction, with dyslalia, have a rich vocabulary, depending on the form of the violation, they can correctly write words and decline them, break them into syllables and develop correct coherent speech.
Speech therapists also distinguish physiological dyslalia, which was described earlier. Such a violation independently passes in children by the age of five and is due to the formation of the most important functions of the body: hearing and speech.
Diagnosis of dyslalia
Diagnosis of dyslalia is a careful history taking. A survey should be carried out not only of the child, but also of the mother. The doctor needs to establish how the period of intrauterine development went, what kind of childbirth was (natural or artificial), whether there were any complications in the process of labor.
At the next stage, the specialist carefully examines the child's medical record and talks with the parents. All this will help to carefully study the patient's past illnesses.
This is followed by a series of tests, after which the doctor will be able to establish how developed the child's psychomotor skills, speech, vision and hearing, and the motor system. And only after that the leading specialist determines the level of development of the articulatory apparatus. This is done visually: the doctor pronounces the words and asks the child to repeat after him. Depending on the correctness of the reproduction of the specified words, a development score will be given.
The main task of a speech therapist is to determine the level of development of a child's oral speech. To do this, the specialist deliberately uses words to follow, which are difficult to pronounce with dyslalia. Additionally, didactic material is used - pictures, toys, objects. After a full check, the doctor can accurately diagnose, indicate the degree and nature of the speech disorder. In addition, a speech therapist conducts phonemic tests to determine hearing.
If the patient has a mechanical impairment of sound pronunciation, then the diagnosis and subsequent treatment should be carried out by a team of specialists, where in addition to a speech therapist there is an orthodontist and a dentist, the child will also need to be examined by a surgeon, possibly a neurologist. In the presence of a disease such as hearing loss, an examination of the ENT is necessary.
Ways to correct dyslalia
The duration of treatment depends on the cause of the dyslalia. If there is a mechanical one, then dental correction of defects is initially performed. It is best to perform these procedures before the age of seven.
Functional dyslalia is corrected by the efforts of a highly specialized speech therapist. Treatment is carried out in several stages. Initially, it is important to prepare the child for the treatment process, to tell why this is being done, what will happen if the problem is not eliminated. Speech therapists during the correction practice methods for the development of not only speech, but also the memory of the child. Particular attention is paid to the differentiation of phonemes by the patient. Regular speech motor skills and articulatory gymnastics, massage are performed.
The next stage of correction is to memorize the child and set the correct pronunciation of sounds. This is achieved through the method of imitation. The last stage is the development of the child's communication skills.
It is important to be systematic in the process of correcting a child's speech. If the dyslalia is of a simple form, then it will take a maximum of 3 months to correct. In difficult cases - about 6.
Forecast for recovery and preventive measures
More than 95% of children fully restore their speech function. Depending on the degree of complexity of dyslalia and the regularity of corrective exercises, the recovery period ranges from 3 to 6 months.
If we talk about preventive measures, here parents need to monitor the health and development of the child. If any deviations in the anatomical structure are found, it is recommended to seek the advice of a specialist.
Not all girls and boys begin to pronounce all sounds immediately and exactly. Some guys have "their own accent" - a specific pronunciation of hissing, whistling, hard and other sounds. Such children are often diagnosed with -, dyslalia - a shorter name for this deviation.
Dyslalia is a common speech therapy diagnosis, which manifests itself in the form of a distortion in the pronunciation of sounds and their omissions.
Definition
Dyslalia - what is it? The unusual term implies a complex of pronunciation disorders, the occurrence of which is not affected by hearing problems or incorrect innervation.
The International Classification of Diseases of the 10th revision explains the concept of dyslalia as specific disorder of speech articulation. Inadequate hearing acuity and mental retardation were excluded as its causes.
In medical documentation, according to the international classification of diseases of the 10th revision - ICD10, this disease appears under the code F80.0
Classification
They are divided into simple and complex dyslalia, based on the number of sounds incorrectly pronounced by the child. With simple ones, he poorly pronounces one sound or one group of sounds that are articulatory similar to each other. When complex - there are problems with different sound groups.
The classification of dyslalia is based on the causes of its development and the features of its manifestation.
There are the following forms, differing in the nature of origin:
- physiological
- functional
- Mechanical
Physiological dyslalia It is diagnosed when everything is in order with the child's speech organs. Incorrect pronunciation of sounds occurs at an early age (up to 5 years), when the muscles of the baby's articulatory apparatus are not yet fully developed.
If after 5 years the violation of sound pronunciation persists, the physiological form of the disease becomes functional.
functional dyslalia arises as a result of organic brain damage or social factors.
Physiological:
- organic brain damage;
- neurological and other chronic diseases;
Social:
- incorrect teaching of speech in the family (lisping, using words in a diminutive form, etc.);
- incorrect pronunciation of sounds by parents and other adults from the immediate environment;
- mixing languages in the family;
Separately allocate mechanical dyslalia, which occurs due to congenital defects of the articulatory apparatus or after an injury.
- Irregularly formed bite or palate.
- Tongue of unusual size.
- Too short or too long bridle, etc.
- Organic dyslalia (another name for mechanical) is a hereditary disease. In this case, a certain speech defect is transmitted from generation to generation.
The functional form is divided into motor and sensory - according to the source of pronunciation failure.
motor dyslalia caused by speech problems sensory- speech-auditory.
Combined forms into which functional dyslalia is subdivided
- articulatory-phonetic;
- articulatory-phonemic;
- acoustic-phonemic
- Articulatory-phonetic dyslalia due to the incorrect location of the organs of articulation. The listener correctly understands the sound uttered by the child, but its pronunciation is far from the norm.
- Distinctive feature articulation-phonemic forms - the replacement of a "difficult" sound with a simpler one, which can be pronounced with less effort of the articulatory apparatus.
- Acoustic-phonemic due to the underdevelopment of phonemic hearing. The child is unable to distinguish the features of specific sounds due to a misunderstanding of phonemes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disorder are manifested in the form of skips, substitutions and distortions of sounds. Localization of violation of sound pronunciation may be different.
Phonetic defects are distinguished by the sounds with which there is a problem. The names of defects are derived from the letters of the Greek alphabet.
- - incorrect pronunciation of hissing [Ж], [Ш], [Ш], [Ч] and whistling [С], [С'], [З], [З'];
- - incorrect pronunciation [P] and [P '];
- Lambdacism - problems with pronunciation [L] and [L '];
- Cappacism - defects in sounds - [K] and [K '];
- Chitism - defects in the sounds [X] and [X '];
- Jotacism - incorrect pronunciation [Y]
- Violation of voicing - observed in pairs "B-P", "D-T", "V-F", "Z-S", "F-Sh", "G-K", etc.;
- Violation of mitigation - replacement of a soft consonant with a paired hard one
A child may have one or more of these pronunciation defects. Speech disorder is often combined.
Diagnostics

The fact that many sounds are not pronounced accurately by a small child is often considered normal by parents. However, the speech features of children with dyslalia - omissions, substitutions, distortion, displacement of sounds - cannot be ignored. If to 5 years old such characteristic speech deviations do not go away - this is already a symptomatology of a serious disorder.
dense interaction with a speech pathologist after a competent examination, it will help to identify the causes of dyslalia, find out why the child speaks inaccurately and prescribe a set of measures to correct speech.
Sedentary and inactive children should be checked for the presence of - a more serious dysfunction, relating not only to sound pronunciation, but also to the vocal aspect in general, the ability to remember and repeat, etc.
Dyslalia and dysarthria are very different from each other. This is due to the fact that in the first form of speech disorder there are no organic lesions, and in the second, the main role, on the contrary, is played by disorders of the central nervous system. Children with dyslalia do not stand out from their peers in much other than "special speech". And children with dysarthria are characterized by an unstable mood, they quickly get tired. They are inactive and poorly acquire new skills.
Differential diagnosis of dyslalia and dysarthria allows you to determine the degree of the state of speech development. The borderline state between them is called erased dysarthria, violations in which are explained by improper innervation of the articulatory muscles. It is quite difficult to diagnose erased dysarthria, since it is similar to both diseases.
Treatment and correction

The diagnosis of "dyslalia" in children and methods for its elimination is the competence of a qualified speech therapist.
The method of speech therapy for dyslalia includes three stages:
- If a mechanical form of the disorder is diagnosed, its causes are removed surgically by a dentist, orthodontist, or surgeon at the preparatory stage. If functional motor dyslalia is detected, priority is given to the development of speech motor skills, and with sensory - to the development of phonemic processes.
- The second stage is devoted to primary pronunciation skills, which are formed, among other things, with the help of imitation and special devices.
- At the third stage of speech correction, the unmistakable use of sounds in a conversation is fixed.
The goal of speech therapy in dyslalia is not only the “installation” of sounds, but also the development of memory and attention, the ability to distinguish sounds and stimulate communication.
Complex dyslalia in preschool children involves systematic sessions with a speech therapist for at least six months, simple - for one to three months.
The method of speech therapy impact on functional dyslalia is designed for three sessions with a specialist per week. And in addition, adults should constantly work with children at home.

In order for your son or daughter not to be among the “far behind” in the ability to speak among their peers, the slightest nuances of their speech must be given close attention. attention.
If you see that the baby can not cope with specific sounds, contact a speech therapist. Most likely, you will need special classes and. And if the examination shows the presence of anatomical problems, you will have to prepare for surgical intervention to eliminate defects.
What the prevention of dyslalia requires from parents, in the first place, is speak well with your children teaching them correct speech by personal example.
The main forms of dyslalia in most cases can be successfully corrected, especially if its activities are started in a timely manner.
However, the treatment of dyslalia is a difficult process and will require great patience, both from the child and from the adults around him. Therefore, it is wiser to place more emphasis on prevention. The sooner minor flaws in pronunciation are identified, the easier it will be to eliminate them.
This diagnosis of a child should not be taken as something frightening. To those close to the baby with “difficult speech,” he only points out that he needs to work much more with him than with his peers.
Dyslalia are pronunciation defects that occur with perfectly healthy hearing and the preservation of the innervation of the speech apparatus. Typically, such verbal deviations can be observed in preschool children and younger schoolchildren. They are manifested by distortion, displacement, substitution or complete absence of one or more sounds of oral speech.
Types of disorders and their symptoms
A term such as “sound pronunciation” covers the phonetic (sound) design of colloquial speech and speech motor skills. Among the various disorders of sound pronunciation, one can most often find individual anomalies in its sound design, while other operations of utterances remain natural. It cannot be ignored that dyslalia today remains one of the most common speech therapy disorders that are not associated with disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system or the hearing aid.
The symptomatology of the disease in each case is determined by a specific form of pathology. In accordance with the classification of the disease, physiological, mechanical (or organic), as well as functional dyslalia are distinguished.
At the same time, physiological dyslalia is caused by the age-related slurring of the child's speech. Mechanical is caused by congenital or acquired abnormalities in the structure and development of the speech apparatus.
Causes of dyslalia
Different forms of the disease can develop due to different reasons. In some cases, these may be violations in the structure of the speech apparatus, in other cases, the disease develops as a result of improper verbal education of the child.
- The physiological form of the disease is based on age-related underdevelopment of organic structures, which can be corrected as the child grows up.
- Mechanical dyslalia occurs due to genetically acquired or congenital pathologies of the organs of the speech apparatus.
- Functional dyslalia is in no way associated with pathologies of the structure of the organs responsible for oral speech. This group is more developed and, in turn, combines several types of disease.

 Functional dyslalia means that the child does not have speech disorders, but he pronounces sounds incorrectly
Functional dyslalia means that the child does not have speech disorders, but he pronounces sounds incorrectly First of all, motor and sensory dyslalia are distinguished.
- The first type develops in connection with functional disorders of the motor speech analyzer. Simply put, with such a pathology, the child's lips and tongue move incorrectly during a conversation - this causes distortion of sounds.
- With sensory dyslalia, the speech-auditory analyzer does not function correctly, which is why the division into component parts of acoustically similar sounds occurs incorrectly and the baby, of course, cannot repeat them correctly.
It also happens that both of the mentioned types of ailment are layered one on top of the other, that is, the child tries to initially incorrectly pronounce the sound he heard, also moving his lips and tongue incorrectly at the same time.
The names of defects in the pronunciation of sounds with a description are given in the table:
There may also be shortcomings in hardness and softening of sounds, when the child replaces soft consonants with double hard ones and vice versa, as well as incorrect pronunciation of voiced and deaf sounds, when deaf consonants are replaced by hard ones and vice versa. In addition, monomorphic or simple and polymorphic (complex) dyslalia can be found. In the first case, the child incorrectly pronounces one sound or several sounds belonging to the same group (we recommend reading:). In the case of polymorphic dyslalia, the pronunciation of several sounds belonging to different groups is always violated.
Most often, the disease does not suffer from the lexical and grammatical side of oral speech. The child develops normally and accumulates a vocabulary that corresponds to his age, perfectly understands what they say to him. However, what exactly he says and answers is in some cases difficult to understand even for relatives.

 The inability to pronounce a certain sound or sounds does not indicate an abnormal development or low level of intelligence of the child.
The inability to pronounce a certain sound or sounds does not indicate an abnormal development or low level of intelligence of the child. Physiological prerequisites for mechanical dyslalia
Mechanical dyslalia often occurs as a result of a short hyoid frenulum, which makes it difficult to move the tongue (more in the article:). The disproportionate size of the tongue itself can also be a reason for the impossibility of developing proper articulation. Various pathologies in the structure of the dentition can also contribute to the development of the disease, such as a strong protrusion of the upper or lower jaw, large gaps in the rows of teeth, an abnormal structure of the palate or its splitting, a shortened frenulum of the upper lip.
Social prerequisites for functional dyslalia
The functional form of the disease can be caused by the following social factors:
- Initially, the wrong speech education of the child. In particular, the frequent copying of "baby talk" by adults and the constant "usi-beads".
- The child is brought up in a family where two languages are spoken. The kid simply transfers the features of articulation from one language to another. As a result, pronunciation suffers when the child speaks both languages. The same can be observed in the case when the child's family speaks one language, and, for example, in a kindergarten, another.
- The auditory perception of phonemes is not sufficiently developed.
- Pedagogical neglect, namely, the situation when parents do not pay attention to the incorrect pronunciation of the child.
- Insufficient mobility of the speech apparatus, which as a result causes incorrect pronunciation of sounds.
- mental deviations.

 Poor communication with a child or, on the contrary, excessive “lisping” can cause the development of functional dyslalia
Poor communication with a child or, on the contrary, excessive “lisping” can cause the development of functional dyslalia Survey
As a result of such an examination, a specialist can draw a conclusion about the presence or absence of pathologies.
The study of the disease begins with the fact that they collect complete information about the course of pregnancy in the mother of the child. The history of the development of the child himself and the illnesses he suffered at different times are carefully analyzed. A speech therapist conducts a visual examination of a small patient, during which he studies the structure and level of mobility of the baby's speech apparatus, after which he offers him to perform several imitation exercises.
The specialist analyzes the level of development of oral speech using didactic materials specially designed to detect pronunciation anomalies. The nature of the violations existing in the baby in various positions is determined. In addition, the phonemic hearing of a small patient is assessed, that is, his ability to distinguish sounds, without which a normal understanding of the meaning of what was said is impossible. When making a diagnosis, not only the form, but also the type of the disease is indicated.
If it is found that the disease is of a mechanical type, the child is referred for a consultation with an orthodontist or surgeon. If the disease is functional in nature, the child will be recommended to consult a pediatric neurologist. And to exclude hearing pathologies, it will be useful to undergo an examination by an otolaryngologist.

 Sometimes an examination by a dentist helps to identify the cause of a speech disorder.
Sometimes an examination by a dentist helps to identify the cause of a speech disorder. Treatment and prevention
Methods for the treatment of impaired sound pronunciation are determined depending on the etiology of the disease.
- In cases of mechanical dyslalia, therapy will be aimed at correcting the bite, surgically correcting the frenulum, etc. The elimination of such defects is carried out in the dental office by an orthodontist. The best age at which such pathologies can be corrected is 5-6 years.
- Treatment of functional dyslalia consists of several stages, which are carried out under the supervision of a speech therapist. In order to interest the child in learning, during the preparatory stage of treatment, much attention is paid to the use of special pedagogical techniques. In particular, various methods of developing concentration of attention and memory are used. In addition, some attention should be paid to the development of speech therapy skills (recognition of sounds (phonemes), etc.).
- The motor type of the disease requires specific classes with the child, focused on improving speech motor skills. This is a special speech therapy massage, special articulatory gymnastics for developing the correct pronunciation, and so on (more details in the article:). Not the least important in developing a good pronunciation of sounds is the correct direction of the air stream during pronunciation and the development of fine motor skills.
During the final stage of the treatment of dyslalia, special attention is paid to the psychological component, since the baby's ability to communicate under any circumstances should develop. The importance of pedagogical work for the formation of self-confidence in the child is also great.
The table below provides examples of exercises for developing the pronunciation of individual sounds:
Dyslalia refers to various speech defects that are observed in people with a normally developed articular apparatus and not impaired hearing. The diagnosis of speech disorders (dyslalia) is made on the basis of a speech therapy examination of the patient. Sometimes the help of related specialists is required - an otorhinolaryngologist, a neurologist, a dentist. Treatment of dyslalia is complex and includes several stages.
Types of dyslalia
There are the following main forms of dyslalia:
- simple - the patient incorrectly pronounces one group of sounds;
- complex dyslalia - the patient incorrectly pronounces two or more groups of sounds, this type of disease is also called polymorphic dyslalia.
For convenience, various pronunciation disorders are grouped, each of which is designated by a term derived from one of the Greek letters.
Thus, they distinguish:
- rotacism - the patient has problems with the letter p;
- hitism - problems with the letter x;
- lambdacism - problems with the letter l;
- cappacism - problems with pronunciation of the letter k;
- sigmatism - problems with whistling and hissing;
- gamacism - the patient does not pronounce the letter g;
- jotacism - problems with the letter y.
Depending on the causes, the following types of disease are distinguished:
1. Mechanical dyslalia.
2. Functional dyslalia. It is caused by a violation of the brain or the influence of various social factors on the child. There are several subspecies of this form of the disease:
- sensory functional dyslalia - the patient has no problems with the articular apparatus, the cause of the pathology is defects in the development of hearing and speech centers;
- motor functional dyslalia - caused by problems with the articular apparatus, due to which a person cannot pronounce certain sounds correctly.
Sometimes there is a mixed sensorimotor form of the disease.
In some cases, speech impairment is the norm. It is associated with age-related characteristics of speech perception by ear and disappears on its own after reaching 5 years.

Causes of dyslalia
All possible causes of dyslalia in children can be divided into two large groups:
- Socio-biological. It is known that young children largely copy the behavior and speech of adults, try to imitate them. If parents lisp with a child or communicate little with him, do not pay attention to how his oral speech develops, then this can eventually lead to the development of speech defects.
- Organic. Violations of sound pronunciation in dyslalia are caused by a violation of the structure of the speech apparatus. Any such problem can cause the development of speech defects in dyslalia.
In preschool children, the disease can be caused by age-related causes. In this case, speech defects disappear on their own after a while and do not require special treatment.
However, it is imperative to pay attention to how the child speaks. After all, in the absence of control, physiological dyslalia can eventually turn into a pathological form that requires specialized speech therapy treatment.
In addition, it is at a young age that a child develops communication skills that will play an extremely important role throughout his life.
Symptoms of dyslalia
The main clinical sign of the disease is a violation of the pronunciation of sounds. The most common are gaps, distortion and replacement of sounds.
The child has problems with oral speech, but the level of his intellectual development is fully consistent with his age, there are no developmental delays. The kid builds sentences correctly, his speech is logical and coherent, he knows how to correctly decline words, he has a vocabulary that is normal for his age.
Diagnosis of dyslalia
Diagnostics is complex and includes the following main steps:
- Collection of anamnesis. The doctor conducts a survey of the patient and his parents. The specialist is interested in whether the mother had any problems during pregnancy (threat of miscarriage, infectious diseases, and so on), how the birth went (whether they were natural or did a caesarean section, did the child receive head injuries during or immediately after them, and etc).
- Examining the patient's medical record. The doctor studies what diseases the baby has suffered, and whether there are any pathologies among them that can lead to the development of speech disorders.
- Various tests, during which the specialist determines the level of development of speech, psychomotor, ODA of the patient.
- Assessment of the level of development of the child's speech apparatus.
In addition to speech, the specialist uses additional materials in the diagnosis.
If the cause of a speech disorder in a child is organic disorders of the speech apparatus, then in addition to the speech therapist, other specialists (dentist, orthodontist) should also participate in the process of diagnosis and treatment. In addition, the child may need to be examined by a neurologist and a surgeon. If during the examination the patient was diagnosed with hearing loss, then an examination by an otorhinolaryngologist is necessary.
Before moving on to methods for eliminating dyslalia, it is necessary to determine the causes that led to the patient's speech disorder.
Correction of dyslalia of mechanical origin takes place in several stages. First, the patient undergoes an operation, during which the anatomical defects that interfere with normal speech are eliminated.
Most often, such an operation is necessary for adults after receiving severe injuries of the jaws and other organs that make up the speech apparatus.
If the organic form of the disease cannot be cured by surgery, then speech therapy is necessary for dyslalia.
In this case, the patient works with a speech therapist, performing special corrective exercises to normalize speech. The most difficult therapy is complex dyslalia in children, in which the child cannot correctly pronounce 4 or more groups of sounds.
With this form of the disease, phonemic hearing is usually impaired in a child, so treatment is primarily aimed at improving the ability to distinguish and perceive sounds. After this goal is achieved, speech correction begins.
It is very important that not only the speech therapist, but also the parents work with the child. Right speech should sound in the house. No need to repeat after the child his incorrect pronunciation. On the contrary, you should pay his attention to errors in speech and teach the baby to pronounce the words correctly.
Since dyslalia includes many different speech defects, the exercises for correction will be different.
Exercises in the treatment of dyslalia are aimed at the development of the speech apparatus. For this purpose, the following methods can be used:
- exercises for the development of fine motor skills;
- speech therapy massage;
- increased hearing sensitivity;
- teaching the child the basics of proper breathing.
When the child has mastered certain general speech skills, the speech therapist begins point correction aimed at teaching the child the correct pronunciation of certain sounds with which he has certain problems.
To achieve these goals, various speech therapy methods have been developed. It is advisable to build classes in a playful way so that the baby does not lose interest in them. The doctor and the child play, talk, read books, sing songs, learn poetry and so on.
It is very important that dyslalia correction classes are carried out on a regular basis (at least 2-3 times a week). In addition, the child must be engaged at home, completing the tasks that the specialist gave him. The duration of therapy depends on the severity of dyslalia and lasts an average of one month to six months. In adults, this period can be significantly less, since it is much easier for them to follow all the recommendations of a speech therapist.
Prevention of dyslalia
The disease is most often successfully treated. The sooner the correction begins, the higher the child's chances of getting rid of speech defects.
In order to avoid the development of this pathology, it is necessary to diagnose and correct organic defects of the speech apparatus in a child in a timely manner. In addition, parents should pay more attention to their baby, deal with him, avoid stressful situations.
You should not lisp even with babies, you need to talk to them like adults, clearly pronouncing all the sounds. If the child does not pronounce some words, then you do not need to repeat the funny mispronunciation after him. On the contrary, you should pay attention to the baby that he says this word incorrectly and teach him the correct pronunciation.
Health to you and your children!
Video about the most common pronunciation defect - "burr" (throat sound r):
- age-related imperfection of sound pronunciation in children of primary and secondary preschool age. It is expressed in sound substitutions, omissions and mixtures. In this case, all substitute sounds are pronounced normatively. There is a softening defect, omissions of consonants during confluence. It is combined with the unformed grammatical structure and coherent utterance. Recognized as part of counseling the child with a speech therapist. Does not need special pedagogical correction, disappears on its own after five years. To prepare the peripheral organs of speech, it may be recommended to perform special articulation exercises.

General information
Physiological dyslalia (age tongue-tied tongue) is a natural stage in the speech ontogenesis of every normally developing child. This condition in speech therapy is not regarded as a speech pathology, however, it is specially distinguished for differentiating the speech norm from deviations. All shortcomings in sound pronunciation - elision, substitution, mixing of sounds - are temporary, transient. The upper age limit of the physiological imperfection of speech is 5-6 years. According to recent studies, only 22% of preschoolers have a purely age-related peculiarity of sound pronunciation, the rest of the children have pathological forms of sound pronunciation disorders (mechanical or functional dyslalia, erased dysarthria), which do not go away as the child grows up on their own and require speech therapy correction.

Causes of physiological dyslalia
The speech of children under 5 years of age is not yet fully formed, and therefore is not without defects in sound pronunciation. These speech defects have a physiological (age) basis. Imperfections in the sound side of speech in preschoolers can be explained by the following groups of factors:
- Unpreparedness of the speech apparatus(tongue, lips, soft palate, lower jaw). Most of the phonemes do not immediately appear in speech in the correct form. First, the preschooler skips sounds or uses substitute sounds (substitutes) that are already in his speech asset. As the muscles of the speech apparatus become stronger, mastering the correct articulation patterns and switching, he gradually masters complex phonemes. At first, pronunciation is unstable: a new sound is present only in some words, and in other cases it is still replaced by a substitute or omitted.
- Poor phonemic awareness. In the younger preschool period, the child is not yet ready to clearly perceive and differentiate all speech sounds. Therefore, a mixture of acoustically similar phonemes is typical for this age stage. By the age of four, the child is already able to notice the acoustic differences between his own imperfect and normative sound pronunciation, so he tries to “pull up” his speech to the model - the speech of adults.
The age from two to five years is sensitive for the development of oral speech. By the end of this period, the speech-auditory and speech-motor apparatuses are already able to correctly perceive and pronounce all the sounds of the native language. In children with an intellectual and speech norm, mastering the sound side of the language occurs by imitation, so physiological dyslalia does not require special intervention.
Stages of learning sounds
The timing and sequence of the appearance of speech sounds in children are due to the physiological readiness of the speech-motor apparatus for their articulation and the speech-auditory analyzer for their perception and discrimination. In the first two years of life, the child learns the pronunciation of vowels ([a], [o], [e]) and labial consonants ([p], [b], [m]) - these sounds form the first words of the baby (" father", "grandmother", "mother"). At 2-3 years old, other vowels that are simple in articulation appear ([i], [s], [y]), as well as labio-dental ([v], [f]), front-lingual ([t], d], [ n]), middle lingual ([th]), back lingual ([k], [g], [x]) sounds. Consonants that are difficult in terms of articulation, requiring precise movements of the tongue and a strong air stream, enter speech from 4 to 5 years: these are whistling ([s], [s], [ts]) and hissing ([w], [g], [h], [u]). Finally, by the age of 5-6, sonoras appear last ([p], hard [l]).
Thus, by the senior preschool period, children completely master the phonemic composition of their native language. After this age, any phonological disorders (even single replacements of correctly pronounced sounds by others) cannot be considered a variant of the norm and need to be corrected. Also, physiological tongue-tied tongue does not include sound distortions (interdental, throat, lateral and other abnormal pronunciation) - these cases are subject to correction at any age from the moment of detection.
Symptoms of physiological dyslalia
During the period of age-related tongue-tied tongue, the child's speech does not sound very legible and clear. This is due to the shortcomings of the pronunciation of individual phonemes: their absence, substitutions for simpler ones or a mixture of acoustically and articulatory close sounds, softening. In addition, there is an imperfection in the grammatical structure and narration.
Among the sound substitutions during the period of physiological dyslalia, the most characteristic is the use of whistling instead of hissing (“masina” instead of “car”, “zouk” instead of “beetle”), front-lingual instead of whistling (“tyanka” - “sledge”). Until a certain age, the sound “r” is completely absent (“eka” - “river”) or is replaced by [y] (“yyak” - “cancer”), by [l] (“head” - “hill”), by [ c] ("pavk" instead of "park"). The middle language sound [th] can also act as a substitute for the sonorant [l] (“jopata” - “shovel”). Instead of back-lingual ones, front-lingual ones are often used (“Dus” - “goose”, “tube” - “cube”). Hard consonants are usually pronounced softly (“zayka” - “bunny”), sometimes soft phonemes are replaced with hard ones (“tota” - “aunt”). Children find it difficult to pronounce consonants - usually one of the sounds is pronounced, the rest are omitted.
Unstressed syllables often “fall out” of the word; in new and complex words, there is a rearrangement of sounds and syllables in places. From about 3-4 years old, children learn the correct use of case endings and prepositions. Coherent speech is formed by the age of 4: complex sentences appear, the child can retell a fairy tale, recite a rhyme. The norm for this age is a violation of the logic of the narrative, a story with abbreviations or excessive detail, inventing and omitting parts of the story. All these shortcomings with physiological dyslalia gradually decrease, and by the age of 6, children's speech becomes correctly designed in phonetic and grammatical terms.
Diagnostics
Usually, at the age of 4-5, children undergo a scheduled preventive examination by a speech therapist in a preschool institution or a children's clinic. During the diagnosis of oral speech, the specialist identifies defects in sound pronunciation and gives them a qualified assessment. To differentiate physiological dyslalia from speech pathology (organic and functional dyslalia, dysarthria, ONR), a comprehensive examination of the child is carried out, including:
- Collection of general and speech history. During the conversation with the mother, the course of pregnancy and childbirth, the presence of birth injuries in the child, and chronic diseases are clarified. Particular attention is paid to speech development - from the first cry of a newborn to the formation of a phrase and coherent speech.
- Inspection of the organs of articulation. During a visual examination, the anatomical structure of the speech apparatus, the presence of malocclusion, tongue, lips, and the structure of the soft and hard palate are assessed. When performing special exercises, attention is drawn to the mobility of the articulatory organs, the volume, accuracy and speed of the movements.
- Auditory differentiation test. To do this, in a game setting, the speech therapist presents paired pictures with the most frequently mixed sounds, asks to repeat after him syllables with alternating voiced and deaf consonants.
- Identification of defective phonemes. With the help of specially selected speech material, the pronunciation of speech sounds is verified when they are in different positions: at the beginning, middle and end of a word. During the test, disturbed sounds and the nature of defects are revealed - omission, replacement, mixing or distortion, voicing / stunning, softening, etc.
- Examination of the lexico-grammatical component and coherent speech. During the survey, visual aids, didactic games and game techniques are used. A speech therapist can ask a child to read a favorite rhyme, tell a fairy tale, make up a story from a picture.
If the child's speech develops in accordance with the age norm, correctional work for physiological dyslalia is not carried out. Sometimes, in order to prepare the speech apparatus for the appearance of sounds, it is recommended to independently conduct articulatory gymnastics under the supervision of parents. The next consultation with a speech therapist should take place at 6-6.5 years before entering school.
Prevention of speech disorders
The prerequisites for mastering normative sound pronunciation are the organization of the correct speech environment in the family and the children's team. From birth, it is necessary to talk with a child, “telling” one’s actions and naming objects that are in the baby’s field of vision. From an early age, it is necessary to instill in the child the habit of looking at the speaker, following the movements of his lips and tongue. Adult speech should be slow, phonetically and grammatically correct. It is strictly not allowed to copy the wrong children's pronunciation. For the development of auditory attention and memory, games for onomatopoeia, memorization of tongue twisters and poems, and reading books are useful.
Pronunciation defects in adults (rotacism, sigmatism, nasality, stuttering), the situation of bilingualism, and the child's stay among peers with incorrect speech adversely affect the formation of children's speech. It is necessary to correct errors in the child's speech at the stage of physiological dyslalia calmly and unobtrusively. In the absence of defects in the structure of the speech apparatus, intact hearing, intellect and innervation of the speech muscles, the preschooler is able to independently, by imitating the correct model, overcome age-related tongue-tiedness.